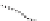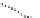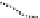Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
The non-repudiation verification key certificate is sent to the verifier along
with the digital signature. The verifier should then perform all the standard
verification checks, which may include checking the appropriate CRLs (see
Section 12.6.5), before verifying the digital signature using the procedure outlined
in Section 7.3.4.
12.6.5
eID key management
The eIDcard scheme provides an interesting example of a keymanagement system
supporting public-key cryptography. We will look at how the eID card scheme
key management is supported, with a particular focus on the two phases in the
certificate lifecycle identified in Section 11.2 as being particularly challenging,
namely certificate issuing and certificate revocation.
eID CERTIFICATES
The eID card scheme key management is based on the closed certification
model that we described in Section 11.3.2. It uses a certification hierarchy, as
described in Section 11.3.3, in order to provide a scalable approach to certificate
issuing. This certification hierarchy is indicated in Figure 12.13. The main CAs
involved are:
Belgium Root CA
. This CA is the root CA that oversees all the eID scheme
certification. It possesses a 2048-bit RSA verification key certificate that is
both self-signed and signed by a commercial CA.
Belgium
Root CA
e
Citizen
CAs
Card
Admin
CA
Government
CA
e
e
e
Server
certificate
NR
certificate
eID card
certificates
e
e
e
e
Figure 12.13.
eID certification hierarchy