Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
EP
3
Imaging Ellipsometer
CE with
degassing channel
WE on
QCM
crystal
RE
QCM crystal holder
Solartron SI 1287
Maxtek
QCM
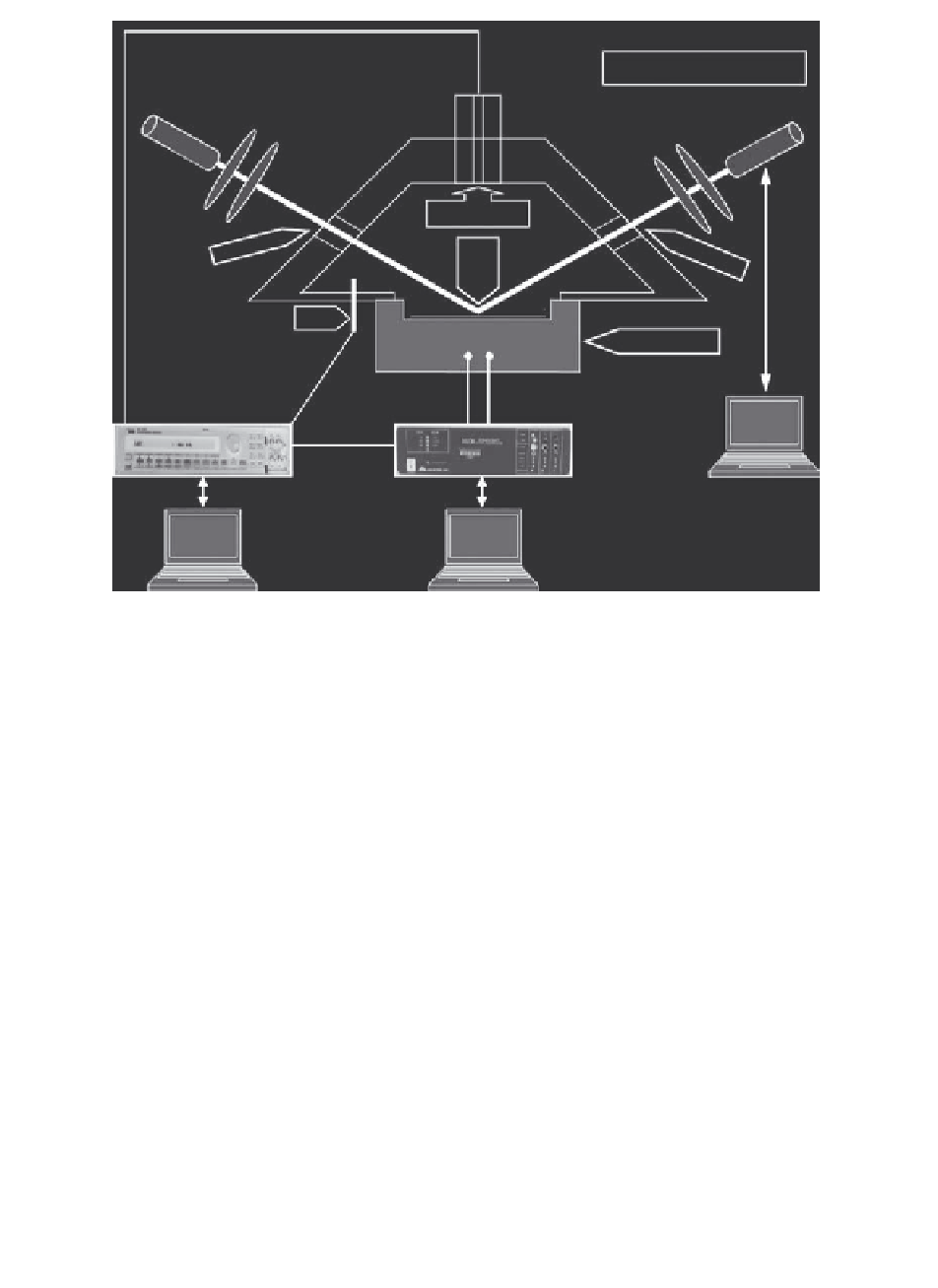
FIGURE 13.12
The experimental setup for the combined electrochemical microgravimet-
ric imaging ellipsometric measurements that can correlate the changes in
mass, electric charge, surface film thickness, optical property, and morphol-
ogy. (Figure 1 in Svoboda, V. and Liaw, B.Y.,
Pure App. Chem.,
80, 2008.
IUPAC. 2008.)
as a device for sensitive mass detection. The application of an external oscil-
lating electrical field on the quartz disk, which is a piezoelectric material, will
induce an acoustic wave that propagates through the disk with the electrode.
When the thickness of the disk is a multiple of a half wavelength of the acoustic
wave, the device will exhibit the minimum impedance and create an oscillation
resonance with a standing shear wave. The ratio of frequency and bandwidth,
called
quality factor
or
Q factor
, can be as high as 10
6
, which provides the
sensitivity in the gravimetric measurement. A common instrument of this type
can offer resolution down to less than 1 Hz with a baseline resonant frequency
on the order of 4-6 MHz. A typical setup for the QCM includes water cooling
tubes, a retaining unit, a frequency sensing unit, an oscillation source, and a
measurement and recording device. Since the shear-mode oscillation acoustic
wave propagates in a direction perpendicular to the crystal surface, the quartz
crystal has to be cut along a few commonly used orientations, so-called the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search