Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
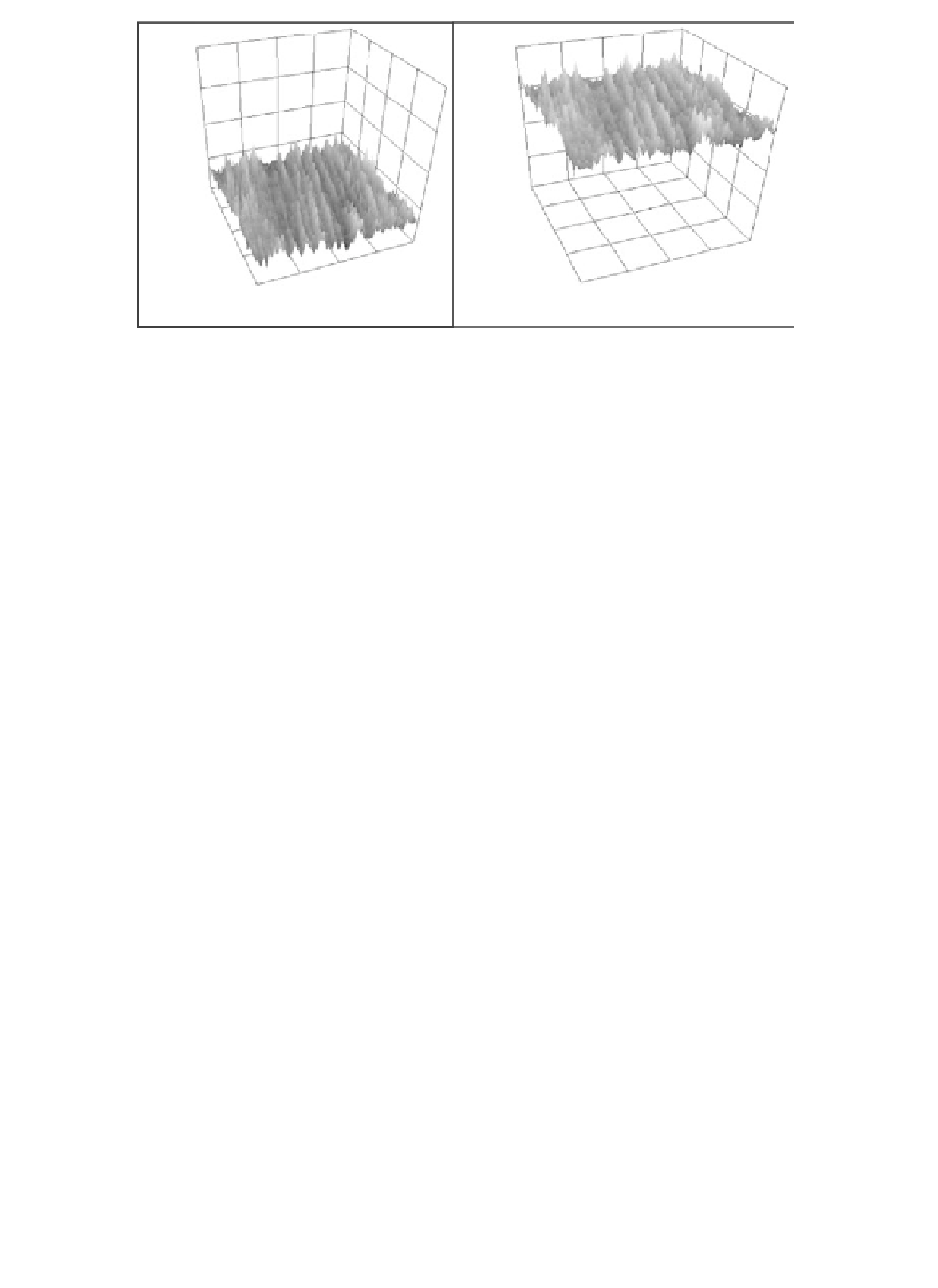
FIGURE 13.11
Surface morphology of a bare Pt electrode surface and the subsequently
deposited poly-methylene green film about 36 nm thick. (Courtesy of the
Svoboda et al.,
Electrochem. Soc.
, 2007.)
oxidation of the biofuels (e.g., methanol, ethanol, lactate, glucose, etc.) cannot
be facilitated. However, the actual deposition process of the poly-azine is much
more complicated than the images show. When combining with microgravita-
tional measurements using QCM during the cyclic voltammetric deposition of
the film (Figure 13.12), the adsorption of a precursor methylene green layer
on the electrode surface was observed (Figure 13.13).
This phenomenon complicated the derivation of the ellipsometric data sig-
nificantly. The evidence of the adsorption was shown in Figure 13.14, which
shows that the progression of the mass change is not in sync with that of
the current. While the ellipsometric angle, ∆ synchronizes with the mass
change, Ψ shows with a different profile, reflecting the nature of the redox
reaction involved in the cyclic voltammetry. More detailed discussion of this
poly-methylene green deposition process has been reported by Svoboda and
Liaw (2008). The mechanism of the deposition can be modeled by estimating
the thickness of the solid poly-methylene green film and the methylene green
adsorption layer on the surface with their respective optical parameters. Fig-
ure 13.15 shows the results of such model simulations at four distinct points of
a cyclic voltammetric deposition to illustrate the changes in the optical prop-
erty due to the thickness changes in the polymer and the adsorption layer,
respectively. This illustration highlights the benefit of such
in situ
characteri-
zation and capability from the imaging spectroscopic ellipsometry in providing
such a superior resolution and accuracy in a noninvasive approach.
13.5.2 Quartz Crystal Microbalance
Quartz crystal microbalance can measure nanograms of mass change on an
electrode surface (Buttry 1991; O'Sullivan and Guilbault 1999). A QCM
consists of a thin quartz disk with electrodes of defined area and property
Search WWH ::

Custom Search