Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
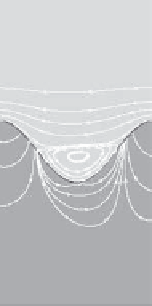
FIGURE 10.9
Streamlines at
t
=T
/
4 (a) and
t
=3T
/
4 (b).
(a)
(b)
(c)
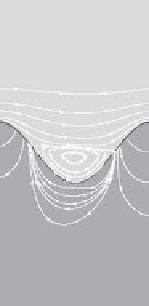
FIGURE 10.10
Solute release in different ripple steepness
s
=0
.
1 (a),
s
=0
.
2 (b), and
s
=0
.
4 (c).
Figure 10.12. This specimen, in common with most from the Atlantic, com-
prises dead and decaying phytoplankton, zooplankton fecal matter, and their
exoskeletons. They sink at rates from a few tens of meters per day to several
hundred meters per day in contrast to phytoplankton cells that individually
sink at no more than 1 m/d and typically 0.1 m/d.
Owing to this rapid sinking, aggregates are known as a vehicle for vertical
flux of organic matter but also hotspots of microbial respiration responsible
for a rapid and ecient turnover of particulate organic carbon in the sea
(Logan and Wilkinson 1990).




Search WWH ::

Custom Search