Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
6
2
5
3
1
7
4
8
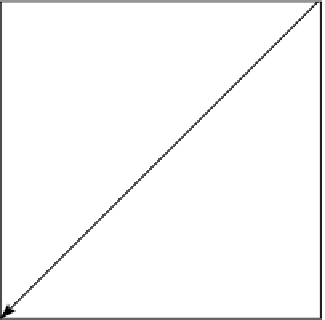
FIGURE 10.1
The lattice direction system for D2Q9 model.
are given by
e
0
= 0 a
n
d
e
i
=
λ
i
(cos
θ
i
,
sin
θ
i
)
c
, with
λ
i
=1,
θ
i
=(
i
−
1)
π/
2 for
4, and
λ
i
=
√
2,
θ
i
=(
i
i
=1
8 (Figure 10.1).
The hydrodynamic variables include mass density (
ρ
), momentum (
j
), and
flux tensor (
Π
), and are computed by the following:
δρ
=
i
−
−
5)
π/
2+
π/
4 for
i
=5
−
f
i
(10.2)
j
=
ρ
u
=
i
e
i
f
i
(10.3)
Π
=
i
e
i
e
i
f
i
(10.4)
Its simplest and by now most popular form is the Bhatnagar-Gross-Krook
(BGK) model, which expresses the collision as a relaxation toward a local
equilibrium, Ω
i
=
f
e
i
), where
τ
is the nondimensional relaxation time
τ
(
f
i
−
−
directly related to the kinematic fluid viscosity
ν
=
c
s
τ −
2
δ
t
and
f
(
eq
)
1
i
is the equilibrium distribution function (Zou et al. 1995; He and Luo 1997;
Dellar 2003):
=
ω
i
ρ
1+
e
i
·
c
s
I
)
u
+
uu
:(
e
i
e
i
−
f
(
eq
)
i
(10.5)
c
s
2
c
s
in which
ω
i
is a weight factor,
c
s
is the speed of sound (set as
c
s
=1
/
3), and
I
is the unit tensor. The weights are given by
ω
0
=4
/
9,
ω
i
=1
/
9 for
i
=1
−
4,
and
ω
i
=1
/
36 for
i
=5
−
8.










Search WWH ::

Custom Search