Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
-
+
(b)
Ca
2+
stores
-
+
Ca
2+
VGCC
Adenylate cyclase
PI-3K
PLC
cAMP/PKA
AChR
rho GTPases
Cytoskeleton
ACh
BDNF
(c)
(d)
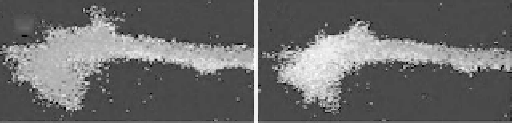
Figure 18.5.
Growth cone changes due to an EF (McCaig et al. 2005). Used with permission
from The American Physiological Society. (See color insert.)
Con A prevented 88% of neurites from responding to a small EF; where without
Con A, 75% of neurites turned towards the cathode (McCaig 1989).
Receptor migration and accumulation can affect the behavior of a cell
partly because of autoregulation. A good example of this is the AChR (yellow
in Figure 18.5). As mentioned previously, AChRs accumulate at the cathode-
facing side of the growth cone. Also at the growth cone, acetylcholine (ACh;
green in Figure 18.5) is spontaneously released, regulating cone growth by
activating nearby AChR. Since AChRs accumulate on the cathode facing side of
the growth cone in an EF, AChR signaling cascades initiate inside the growth





























Search WWH ::

Custom Search