Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
OCP
Ca
8
H
2
(PO4)
6
·5H
2
O
1
2
1
'OH-Ap.'
(
Ca,
Na
,
M
)
10
(PO
4
,
CO
3
,
HPO
4
)
6
(OH,
F
,
Cl
)
2
1
4
DCPD
CaHPO
4
·2H
2
O
-TCP
(Ca,
Mg
)
9
(PO
4
)
6
b
3
2
3
2
ACP
amorphous Ca-P
w/. co
2
3
w/. Mg
2+
and/or P
2
O
4
7
1
4
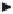
Figure 2.8.
Schematic presentation of the transformation of one type of calcium phosphate
to another [59,64].
O
B
A
B
Figure 2.9.
Crystal growth of calcium phosphates in gel system. (silica gel incorporating
phosphate ions, calcium ions diffusing into the gel), 37 °C, solution Ca/P molar ratio, 1/1.
(1) pH 6.5, OCP (O) spheres grew on the top layer and DCPD platy crystals grew on the
bottom layer of the gel' (2) same pH but in the presence of
P
2
4
−
ions, OCP growth was
inhibited, DCPD crystal size reduced and change in shape observed; (3) in the presence of F
−
ions, growth of OCP and DCPD were suppressed, growth of (F,OH)-apatite needle-like crystals
was promoted [59,64,69].





















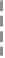





Search WWH ::

Custom Search