Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Beech (axial)
Beech (non-axial)
Poplar (axial)
Poplar (non-axial)
Mahogany (axial)
Mahogany (non-axial)
Red oak (axial)
1.80
1.60
1.40
Sapele (non-axial)
MSA model (axial)
MSA model (non-axial)
1.20
1.00
0.80
0.60
0.40
0.20
0.00
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
Porosity (%)
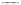
Figure 11.14.
Fracture toughness as a function of porosity for cracks propagating perpen-
dicular (axial) and parallel (non-axial, transverse) to the axial direction of bioSiC derived from
several precursors (error bars equal one standard deviation and arrows refer to the axial direc-
tion). Values predicted by the MSA model for axial and transverse orientations are also shown
by the dashed lines.
50-70% higher than the values measured on porous samples due to the presence
of excess silicon, as expected [Presas, 2005].
The elastic moduli of porous bioSiC determined in compression in the axial
and transverse directions are plotted as a function of porosity in Figures 11.15a
and 11.15b [Kaul, 2006]. By grouping these data by the type of precursor (in this
case, diffuse-porous and ring-porous), it is apparent that the axial stiffness of dif-
fuse-porous SiC are more sensitive to porosity. Porous SiC is signifi cantly stiffer
in the axial direction than in transverse directions, in most cases by one order of
magnitude. A similar trend as the compression strength.
Such behavior is typical of honeycomb materials where the transverse (or in-
plane) strength and stiffness are controlled by cell-wall bending, whereas axial (or
out-of-plane) strength and stiffness depend on compression of the cell walls. The
elastic moduli reported here are about half that reported in the literature for
biomorphic Si/SiC at room temperature [Singh, 2002; Smirnov, 2003; Kardashev,
2005; Kardashev, 2006]. This is not surprising as the unreacted silicon stiffens the
composite.
Martínez et al. [Martínez, 2003] has compared the mechanical properties of
biomorphic SiC with other siliconized SiC. Figure 11.16 shows the strength data
for the reaction bonded SiC (RBSC), reaction formed SiC (RFCS), and BioSiC


















Search WWH ::

Custom Search