Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
While the improvement in wear resistance of the TNZT + 2B material after
oxidation against a substantially harder Si
3
N
4
counterface material is promising, it
is quite likely that in a real implant, such an oxide layer might spall during the
sliding of the femoral head against the internal surface of the acetabular cup, a
highly undesirable attribute. Therefore, the critical issue is to determine the wear
resistance of the TNZT + 2B composite against a softer, more realistic, counter-
face materials, such as SS440C (H
10 GPa). Table 9.2 lists the hardness and
Hertzian contact stresses for both TNZT + 2B and Ti - 6Al - 4V with respect to the
two different counterfaces namely Si
3
N
4
and SS440C. This contacting condition is
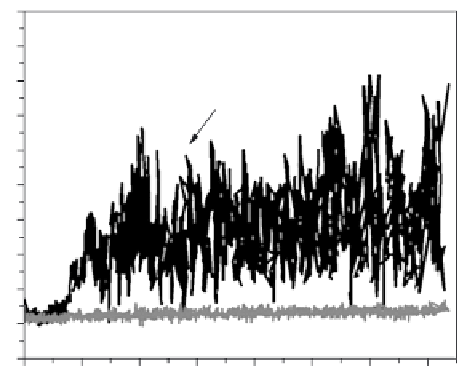
expected to be more representative of an actual ball and socket joint. Figure 9.27
show typical friction coeffi cient curves for the alloys sliding against a SS 440C
counterface ball after removal of the titanium oxide layers by a light mechanical
polish.
The initial friction coeffi cients of both Ti - 6Al - 4V and TNZT + 2B are approx-
imately 0.1, however the friction coeffi cient of Ti-6Al-4V began to deviate at
∼
∼
15 m sliding distance. A continual steady increase in the friction coeffi cient
occurs up to
0.4 to 0.6, similar to the values shown in the as-synthesized condi-
tion in Figure 9.21. These higher and more fl uctuating values suggest increased
abrasive wear and debris generation. In contrast, the initial friction coeffi cient of
TNZT + 2B alloy remained at a very low steady-state value of
∼
∼
0.13 for the entire
test, instead of the high values (
0.6) shown in Figure 9.21 for the as-deposited
condition. Thus, the softer steel counterface eliminated the TiB precipitate
∼
1.0
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
Ti-6Al-4V
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
TNZT+2B
80
Distance (m)
0.0
0
20
40
60
100
120
140
Figure 9.27.
Wear plots showing the friction behavior as a function of distance of Ti-6Al-
4V ELI and TNZT + 2B with SS440 stainless steel counterface balls. [Sonia Samuel et al.
Wear
Resistance of Laser Deposited Boride Reinforced Ti
-
Nb
-
Zr
-
Ta Alloy Composites for
Orthopedic
Implants
(to appear in Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2007)]

Search WWH ::

Custom Search