Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Near UV photo lithography
Micro transfer molding
Micro scale
Micro molding in capillaries
Ordered
Electron beam lithography
Scanning probe lithography
Dip pen lithography
Nano scale
Surface
topography
Electrospinning
Micro scale
Cutting with diamond tool
Polymer demixing
Unordered
Phase separation
Electrospinnig
Nano scale
Colloidal lithography
Chemical etching
Self assembly
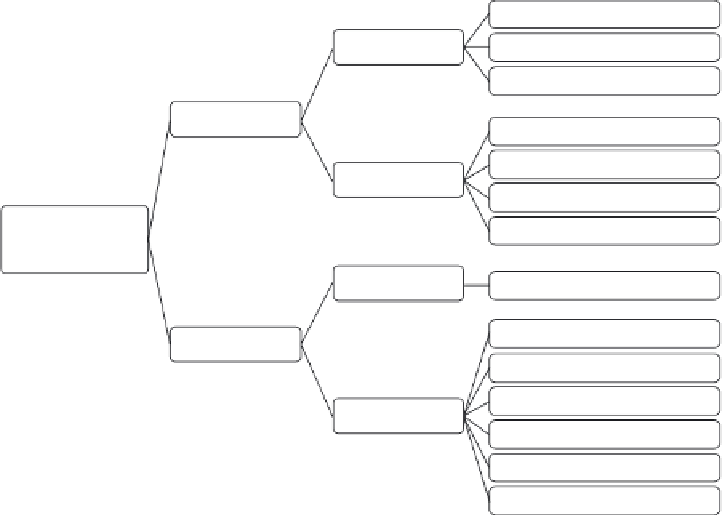
Figure 8.9.
Schematic representation of types of topographical modifi cation and techniques
used for their fabrication.
8.4.1.2.2 SURFACE TOPOGRAPHY [48, 75 - 78] . Addition or subtraction of
material at the surface leads to surface roughness. Although photolithography
has been widely used for generating surface topographies, new methods that al-
low for more precise control of topography at the micro/nano scale [Figure 8.8
(C-H), Figure 8.9] have also been developed.
As previously stated, surface topography can signifi cantly infl uence cell
behavior and as a consequence biomaterial-tissue interaction and eventual device
integration with tissue. Hence, a variety of methods have been developed for the
modulation of surface topography including plasma methods. Among the plasma
methods, a wide choice is available for use, such as plasma sputtering and etching,
plasma implantation, plasma deposition, plasma polymerization, laser plasma
deposition and plasma spraying. The main advantage of surface modifi cation
using plasma-based techniques is that they do not affect the bulk properties or
composition of the biomaterial [85]. Table 8.4 lists some of the surface topography
modifi cations [16, 20, 22, 84] that have been reported for biomaterials.
Contrary to the belief that surface modifi cations can signifi cantly infl uence
cell response, there have been reports that surface modifi cation may not infl uence
biointegration or biomaterial host tissue response. Parker et al. studied implants
that were surface treated with RFGD plasma or fi bronectin coating and demon-
strated that none of the surface treatment methods signifi cantly infl uenced tissue
reaction around the implant [14]. In a similar study with surface modifi ed silicon
Search WWH ::

Custom Search