Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
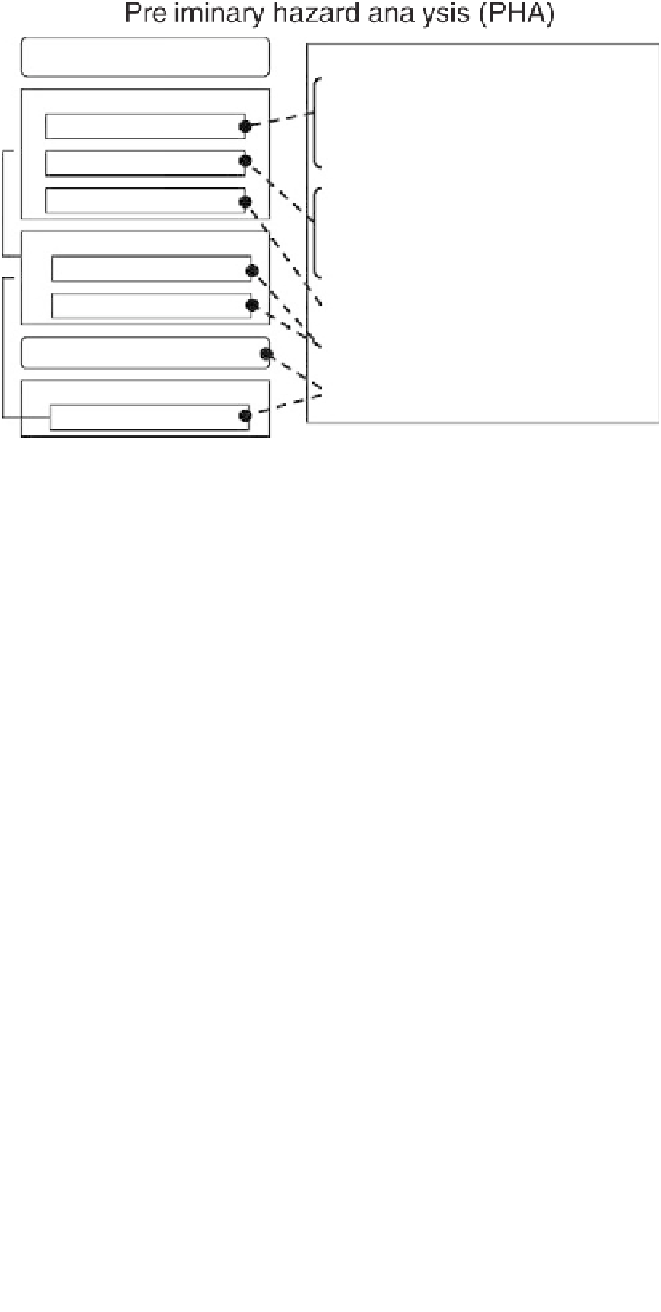
Initiate
quality risk management process
PHA
1. Define boundaries
Risk assessment
2. Hazard identification
Hazard identification
U
n
a
c
c
e
p
t
a
b
l
e
3. Identify causes and major effects
Risk analysis
4. Determine severity of effects
5. Estimate likelihood of occurrence
Risk evaluation
Risk control
6. Suggest corrective/preventive measures
Risk reduction
Risk acceptance
7. Qualitative ranking
8. Recommend mitigations
Output/report and implementation
Risk review
9. Implement and update
Review event
Figure 2.2
How preliminary hazard analysis fits in the risk management process.
2.4.2 Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Failure Mode Effects and
Criticality Analysis (FMECA)
2.4.2.1 Description
A failure mode effects analysis (FMEA) is a systematic
inductive risk analysis of a system to identify the potential failure modes, their
causes and effects. An FMEA may also be the procedure by which each potential
failure mode in a system is analyzed to determine the results or effects thereof
on the system and to classify each potential failure mode according to its sever-
ity. An FMEA requires product and process knowledge. It can be applied to a
manufacturing operation to analyze the effect on product or process [4].
In addition to FMEA, there is also failure modes, effects, and criticality anal-
ysis (FMECA). FMECA is an extension to the FMEA to include a means of
ranking the “criticality” of the failure modes to allow prioritization of controls or
mitigations. It is not uncommon that the terms FMEA and FMECA are used inter-
changeably. However, by definition, FMEA stops with scoring severity and prob-
ability of occurrence. If it involves matrices (for ranking and prioritization), risk
priority number (RPN), or ranking, the failure analysis is technically FMECA.
The primary elements of an FMEA or FMECA include the following:
1. Define the question/system boundaries.
2. Identify potential failure modes.
3. Identify failure effects (and causes).
4. Determine severity of effects.
5. Estimate likelihood of failure mode occurrence.




















Search WWH ::

Custom Search