Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
vascular system.
48
The cardiomyocytes in this case were grown on a light-
addressable potentiometric sensor (LAPS), which monitored extracellular
fi eld potential. Changes in the beating frequency, amplitude and duration
indicate the effect of heavy metal ions including mercury and lead. Biosen-
sors based on the growth of cells on electrodes and measurements of elec-
trical impedance have been investigated for many years.
49
Such biosensors
have been used to investigate the barrier properties of vascular endothelial
cells
in vitro
.
50,51
Loss of vascular endothelial integrity has been implicated
in a variety of conditions, including ischaemia, arteriosclerosis and infl am-
mation. The disruption of endothelial integrity of a layer of cells cultured
on electrodes can be correlated with measurements of transendothelial
electrical resistance (TER). Tiruppathi
et al.
50
showed a dose-dependent
decrease in impedance due to the addition of
-thrombin to a cultured layer
of bovine pulmonary microvessel endothelial cells, which could be pre-
vented by pretreatment with a protein kinase C inhibitor. Wegener
et al.
51
showed that increased TER after
α
-adrenergic stimulation was mediated
by an increase in intracellular cAMP. Abdelghani
et al.
52
investigated the
effect of infl ammatory agents on the electrical impedance of human umbili-
cal vein endothelial cell monolayers. These examples illustrate how such
cell-based biosensors could be used for drug development, by illuminating
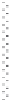
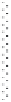
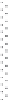
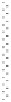
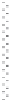
signal-transduction pathways. A typical experimental set-up used in these
kinds of experiments can be seen in Fig. 11.9. The advantage of such cell-
based biosensors is the physiologically relevant functional information that
β
Endothelial cells growing on
electrodes and surface of
tissue culture dish
Electrical current passing
between and through cells
Tissue culture medium
Gold measurement
electrodes
Impedance analyser
11.9
Typical experimental set-up for measuring transendothelial
resistance (TER), using gold electrodes evaporated onto the surface
of a tissue culture dish. TER is dependent on the passage of current
between cells and through cell bodies, which is determined by
cell layer structure, and can be changed by the addition of drugs,
toxins etc.














































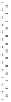

































Search WWH ::

Custom Search