Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
fl exibility. Some fabric grafts also incorporate an external support coil to
resist kinking as well as external compression, a desirable feature in extra-
anatomical bypass such as axillofemoral bypass. These grafts are usually
not crimped.
8.4
Intimal hyperplasia
Early failure of vascular prostheses, within days of surgery, occurs mainly
because of technical errors, especially when the recipient artery is very small
and friable, or thrombosis. After the initial post-operative period, graft
failure commonly occurs as a result of intimal hyperplasia (IH) develop-
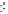
ment, normally at critical points within the distal end-to-side (ETS) anas-
tomosis. These points correspond to the graft heel, toe and recipient artery
fl oor (Fig. 8.1), where areas of separation and fl ow division occur resulting
in abnormally low wall shear stress (WSS), an important factor in the devel-
opment of hyperplasia (Sottiurai, 1990; Sottiurai
et al.
,
1994).
The intima of an artery consists of an endothelial monolayer covering
the internal elastic lamina, which, in turn is surrounded by smooth muscle
cells (SMC) and the outermost loose connective tissue of the adventitia.
The intimal response to trauma is well documented, whereby a thick neo-
intima develops due to the proliferation of EC in conjunction with the
migration of SMC from the underlying media through the elastic lamina.
The subsequent proliferation of these cells with secretion of a tough extra-
cellular collagenous matrix creates a characteristic histological appearance
of an intimal layer of SMC within an abundant stroma, resulting in an
overall reduction in lumen and increase in wall thickness. Such cellular
activity in response to local trauma has important implications in the genesis
of both atheromatous plaques and IH. The aetiology and mechanisms by
Graft
To e
Heel
Recipient
artery
Floor
8.1
The distribution of IH in the ETS distal anastomosis (after
Sottiurai, 1990).




































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search