Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2.3 refraction
We.can.also.calculate.the.path.a.ray.of.light.will.take.when.it.passes.through.an.interface.that.separates.
media. with. two. diferent. indices. of. refraction.. he. speed. of. light. inside. the. media. with. an. index. of.
refraction.
n
.is.
c
/
n
,.where.
c
.is.the.speed.of.light.in.vacuum..Since.
n
.>.1,.the.speed.of.light.is.always.slower.
in.media.other.than.vacuum..Given.this.speed.of.light.within.the.media,.we.can.then.calculate.the.time.
that.light.takes.to.travel.from.a.point.
A
.in.the.irst.medium,.with.index.
n
1
,.to.a.point.
B
.in.the.second.
medium,.with.index.
n
2
,.as.shown.in.Figure.2.2.
he.time.
t
.required.for.the.light.to.travel.from.point.
A
.to.
B
.along.this.path.is.given.by.the.following.
equation:
n
c
d x
n
c
d L x
1
1
2
t x
( )
=
( )
+
(
−
)
=
c
n d x
(
( )
+
n d L
(
−
x
))
1
2
1 1
2 2
(
)
1
(
)
2
=
c
n h
2
+
x
2
+
n
h
2
+
L x
−
1
2
.
To.ind.the.minimum.time,.we.take.the.derivative.of.
t
.with.respect.to.
x
.and.set.it.equal.to.zero,.which.
gives:
d
t x
x
( )
d
1
1
2
1
2
−
1
2
=
(
)
−
1
2
(
)
(
)
+
(
)
2
(
)
=
n
h
+
x
2
x
n
h
+
L x
−
−
2
(
L x
−
)
0
2
2
2
1
2
c
x
L x
−
=
n
−
n
1
2
h
2
+
x
2
(
)
2
h
2
+
L x
−
(2.3)
x
d
L x
d
−
=
n
−
n
1
2
1
2
=
n
sin(
θ
)
−
n
sin(
θ
)
1
1
2
2
n
sin(
θ =
)
n
sin(
θ
)
.
.
.
1
1
2
2
We.recognize.this.as.Snell's.law.from.Chapter.1.
A
d
1
h
1
n
1
θ
1
x
θ
2
d
2
n
2
h
2
L
−
x
B
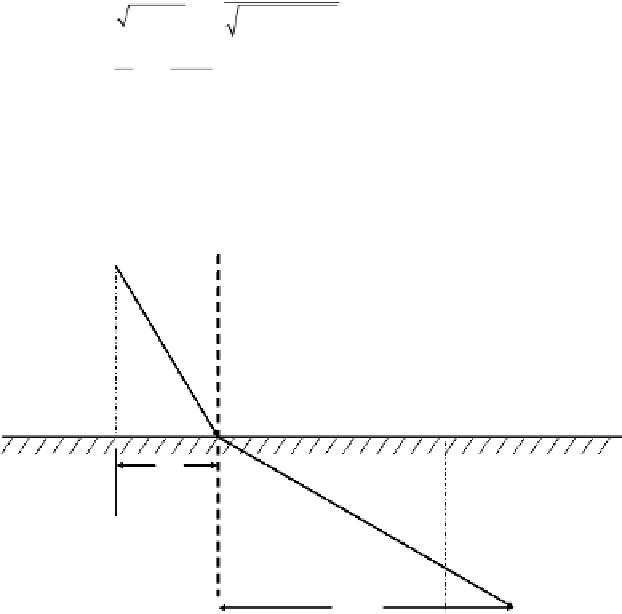
FIGuRE 2.2
Refraction.of.the.light.through.an.interface..he.light.from.point.
A
.is.incident.at.an.angle.θ
1
.on.an.
interface.between.two.media..he.upper.media.has.an.index.of.refraction.
n
1
.and.the.lower.media.has.an.index.of.
refraction.
n
2
..he.change.in.the.index.bends.the.path.of.the.light.at.an.angle.θ
2
,.causing.it.to.pass.through.point.
B
.