Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
number of additional bacterial types and biochemical pathways play a role in
the overall breakdown process. As with composting, there is much interaction
between these various organisms.
Applying AD to Waste Management
The nature of AD inevitably means that its applications to waste management
are relatively large scale operations, there being no effective equivalent of home
composting. Hence, whether the application is as an on-site treatment for process
effluent or as part of a centralised municipal waste initiative, the approach relies
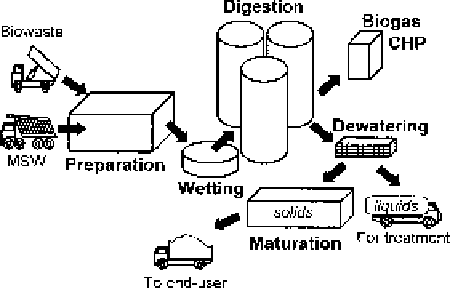
heavily on engineering, a schematic plant being shown in Figure 8.2. This is in
clear contrast with composting and, together with the attendant additional costs,
probably goes further to explain the overall lower take up of this technology than
any other factor. It should also be apparent that more resources, and primarily
a more skilled workforce, are essential prerequisites for success. However, for
wastes which are particularly suited to this form of biotechnology, a number
of cost benefit analyses over the years have shown that these drawbacks may
often be outweighed by the advantages inherent in the system. As with so many
practical applications of environmental biotechnology, there is seldom one catch-
all solution and the most appropriate approach can only really be judged on the
specifics of the problem. There will always be cases when either composting or
AD is self-evidently the most suitable route; when the matter is less clear-cut,
however, the technology decision is often much more difficult to make.
There are many ways in which AD systems may be categorised as will be
briefly discussed below. However, it is important to realise that, irrespective of
their individual construction, they all fundamentally consist of isolated vessels
of some kind, designed to exclude air and maintain internal conditions at the
optimum for bacterial action. It is possible to describe systems treating slurries
of 15% total dry solids (TDSs) or less as 'wet', or 'dry' if their TDS exceeds this
Figure8.2
ADplantschematicflowchart
Search WWH ::

Custom Search