Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Bioventing
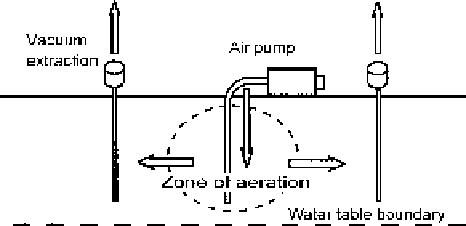
Bioventing is a technique used to remediate contamination above the water table
boundary, and again a generalised diagram appears in the following Figure 5.5.
This process also involves super-aeration, again with the intention of stimulating
accelerated breakdown of the pollutants present, though this time it is taking
place within the soil itself, instead of the groundwater. Bioventing is not generally
suitable for remediating sites with a water table within 1 m of the surface, nor for
heavy or waterlogged soils, since air flow is compromised under these conditions.
Air is introduced from a compressor pump, via a central pipe, or set of pipes,
dependent on the size of the area to be treated, down into the region of contami-
nation. The extra oxygen availability thus achieved, as in the previous approach
described, stimulates the resident microbes, which then treat the polluting sub-
stances. The air flow through the soil is further driven by vacuum extractors
peripheral to the treatment zone, which increases the dissolved oxygen levels of
the soil water and thus facilitates uptake by the native micro-organisms. Volatile
compounds, which are either present as part of the original contamination, or
generated as by-products of the biological treatment, are often mobilised during
processing and thus more easily extracted. However, in many practical applica-
tions, the air extraction rate is adjusted to maximise decomposition underground,
thus reducing a separate requirement for surface treatment of volatile compounds.
As with the biosparger, control devices typically regulate the pressure,
filters clean particles from the intake and the flow rate is monitored in
operation, with data loggers and telemetry systems again featuring in the more
complex applications.
Unsurprisingly, bioventing also requires extensive and comprehensive site
investigation before commencement, not least because the proper positioning
of the necessary system of pipework is essential to the proper functioning of
this technique.
Injection recovery
The injection and recovery method, for which a generalised diagram appears in
Figure 5.6, makes use of the movement of ground water through the zone of
Figure5.5
Bioventing
Search WWH ::

Custom Search