Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Etched-mirror laser
(facets reflection coated)
CAP (GaAs)
layer
Cladding (GaAlAs)
Active (GaAs)
Passive
waveguide (GaAlAs)
Waveguide
isolation (GaAlAs)
Semi-insulating
GaAs substrate
Light
output
Etched mirror reflector
output coupler
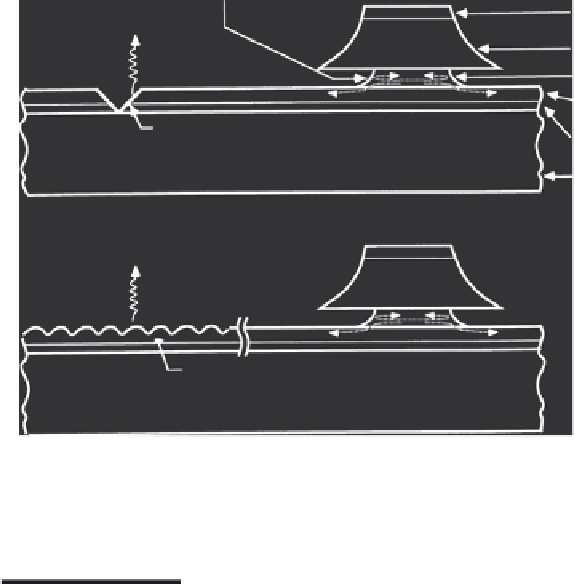
Etched-mirror laser with etched mirror reflector output coupler
(a)
Light
output
Grating
output coupler
(b)
Etched-mirror laser with grating output coupler
FIGURE 2.30
Surface-emitting laser using (a) etched V-groove and (b) grating.
2.6 OpticalInterconnectMedia
Optical interconnection of LSI chips requires a passive distribution network
to transmit optical information from one point to another. To permit the gen-
eral interconnection of one transmission point with other reception points
in the system, the data are transmitted in a data packet from the various
transmitters. As a result, the information is contained in a burst of bits, some
of which indicate the destination, others the sender, and others the data to be
transmitted. The nature of the transmission can be point to point or global.
As a result, it is required that the optical interconnect medium permits effi-
cient distribution of optical energy to all the required ports, with a minimal
loss due to coupling and insertion loss of the optical signal. Furthermore,
the dimensions of this optical medium must be compatible with the sizes of
typical integrated circuits and systems utilizing such circuits.
2.6.1 Guided Wave Interconnects
The guiding of light for transmission via optical fibers is accomplished by
confining the optical energy in a core region that is surrounded by a clad-
ding layer of lesser refractive index. This refractive index profile from the
Search WWH ::

Custom Search