Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Collection
apertures
Display/control module
(NTE .08 m
3
& 30 LB.)
Fiber/optic
bundles
Alpha/
numeric
display
Foclwr
control
electronics
µ Processor
non-volatile
memory
Wavelength
&
pulse width
I/D &
processor
Signal
amp
&
condit.
Inp
ut
120 VDC
60 Hz
Power
supply
Detectors
(4-6)
Filter
Threat/
parameter
library
(NTE .06 m
3
& 40 LB.)
Detector/electronics module
Lap top computer
Display/
keyboard/
CPU
P/O
DCM
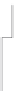
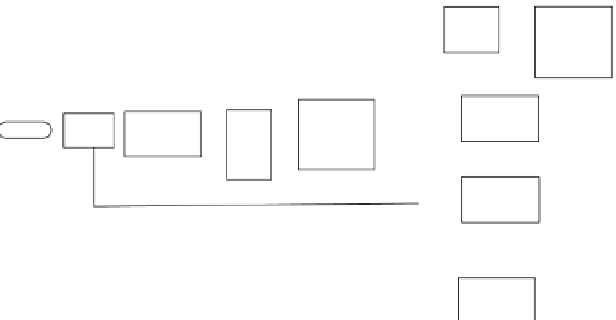
FIGURE 4.30
LWR block diagram.
spectrally dispersed to two linear fiber arrays. Each array will be integrated
with discrete detectors. The fiber array located at the grating focal plane
will utilize zero order diffraction elements to determine quadrant detec-
tion of arrival, while the second array responds to first-order dispersion for
wavelength identification. The advantages of this grating arrangement are
reduced background clutter as seen by individual detectors and discrimi-
nation against false alarms caused by solar glint, chopped sunlight, gun
flashes, and strobe lights. The light from broadband sources such as sun-
light will be spread over several detectors. Conversely, laser radiation will
illuminate one or at most two adjacent detectors. Simple electronic logic will
be used to discriminate between laser and nonlaser sources.
4.19.4 System Configuration
The proposed LWR design makes the use of optical fiber bundles to cou-
ple laser energy from the outside world to a detector electronics module
(see Figure 4.31). Fiber-optic implementation offers many advantages. The
removal of detectors and preamplifiers from the skin greatly simplifies the
task of eliminating EMI effects. We also have flexibility in locating the detec-
tor electronics package, reducing installation and space constraints, and
facilitating environmental hardening. Since the input apertures are small,
locations for mounting with an unobstructed field of view are more easily
found. Small input apertures also result in low optical and radar cross sec-
tion and minimal aerodynamic disruption. Finally, the elimination of heavy
electronic interconnecting cables and multiple detector packages should
result in reduced system weight.












































Search WWH ::

Custom Search