Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
GaAIAs laser
Modulator
RF power IN
Low noise amplifier
Optical
fibers
Photodiode
GaAs MMICs
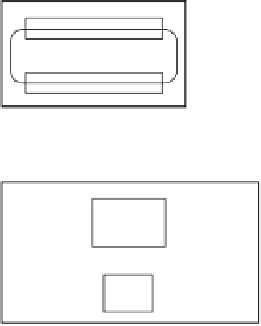
FIGURE 2.1
Optical signal distribution network for MMIC module RF signals.
by the need for faster computing systems have pushed the requirements on
various levels of interconnects to the edge of what is possible with conven-
tional electrical interconnects. The first trend is the development of higher
speed and denser switching devices in silicon and GaAs. Switching speeds
of logic devices are now exceeding 1 Gb/s, and high-density integration has
resulted in the need for interconnect technologies to handle hundreds of
output pins. The second trend is the development of new architectures for
increasing parallelism, and hence throughput, of computing systems.
A representation of processor and interconnect complexity for present and
proposed computing architectures [6] is shown in Figure 2.2.
The dimension along the axis is the number of processors required for
various architectures. On the left side is the Von Neumann architecture
Increasing interconnect complexity
Coarse
Fine
Cosmic cube
DADO
Neural networks
P
= 10
6
Conventional
Von Neumann
P
= 2-4
P
= 256
Massively
parallel
Cray/CDC
MIMD machine
butterfly
Connection machine
Increasing processor complexity
FIGURE 2.2
Processor versus interconnect complexity.
























Search WWH ::

Custom Search