Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Modulation frequency = 1 GHz
Modulation frequency = 3 GHz
No
modulation
Optical
modulation
depth= 80%
80%
90%
90%
100%
100%
(a)
Modulation frequency = 1 GHz
Modulation frequency = 3 GHz
No
modulation
70%
80%
70%
80%
>90%
>90%
(b)
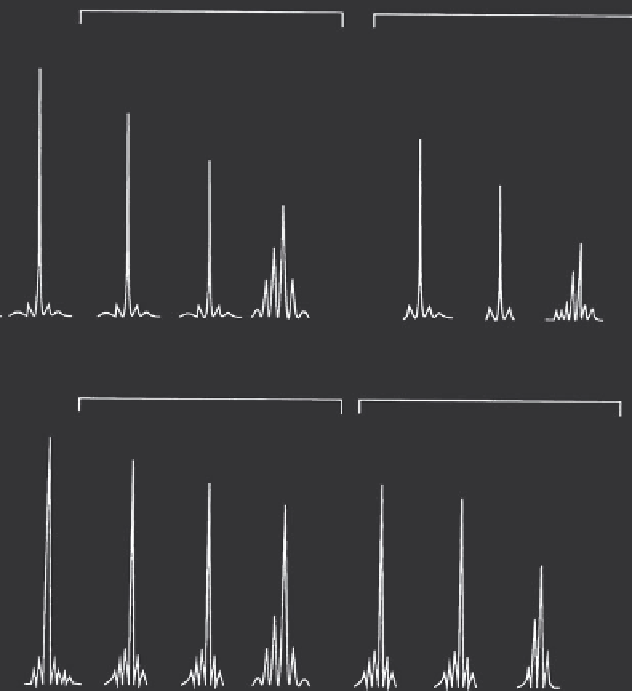
FIGURE 4.21
(a) Observed time-averaged spectrum of the laser shown in Figure 4.20 under microwave mod-
ulation at various optical modulation depths, at modulation frequencies of 1 GHz. The laser is
biased at a dc optical power of 1.5 mW. (b) Same experiment as in (a) but for the laser shown in
Figure 4.21.
It would appear that stable laser operation can be ensured by increasing
the bias, but other undesired effects occur with increasing bias. These effects
include temperature instability and line broadening due to the effect of light
reflected into the cavity from external sources. The temperature instability
results mainly from shifts in the bandgap with temperature, whereas the
line broadening results when intensity within the laser cavity is increased
above a critical level.
The method described for maintaining single-mode operation through
reduction in the modulation depth may in some cases result in satisfactory
system performance; however, evaluation of the overall system performance
Search WWH ::

Custom Search