Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
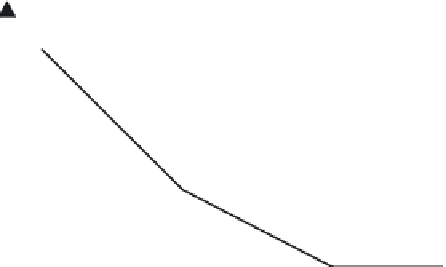
τ
T
s
PW
FIGURE 3.12
Sensitivity of Bragg cell receiver versus pulse width.
Another dynamic range enhancement technique uses a Mach-Zehnder
interferometer (MZI) system. This approach is illustrated in Figure 3.13.
The optical beam is split between two Bragg cells. The first of these is
driven by the signals to be analyzed. The second is driven by a local
oscillator reference waveform producing diffracted output reference
beams which are recombined with the diffracted signal beams and then
focused on the PD array. The beam recombiner is arranged to angularly
shift the diffracted reference beams by a small amount so that the resul-
tant interferometric mixing produces output signals at some intermedi-
ate frequency IF which is the same for all PD's. The heterodyned output
signals are then bandpass filtered to provide immunity against DC light
levels and improve discrimination against detection channels. As the
PD heterodyne signal power is now proportional to the RF signal input
power, the dynamic range is greatly improved [25].
This technique was accomplished using bulk techniques and has yet to be
implemented using IO techniques.
3.6 PhotodetectorReadoutTechniques
Information readout schemes embrace several different parameters. These
include PD integration time, number of PDs, and pel access time. The access
time and the integration time are usually matched, but a compromise must





Search WWH ::

Custom Search