Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
(c)
Cr
Ca
LRa
M
Ao
A
Elastin
Collagen
LDL
(d)
a
a
b
b
B
Elastin
Collagen
LDL
Figure 13.9
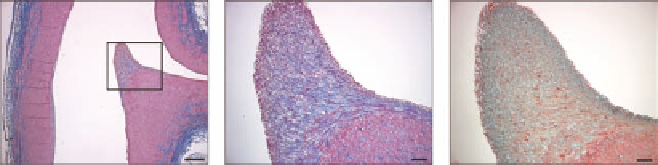
LDL binds to the atherosclerosis-susceptible renal artery ostial diverter at the aortic entrance to the
renal artery. (a, b, c) Histological analysis. Sagital sections of renal diverter stained with Masson's trichrome stain
(a, b) for collagen (blue) and smooth muscle (red), and Movat stain (green) for proteoglycans (c). The caudal aspect
(Ca) of the renal ostium (a) is thickened, angulated, and more rigid than the cranial aspect (Cr). Both the intimal
(rectangle) and medial (
M
) layers of the caudal renal ostium are thickened, forming a flow diverter at the entrance
to the renal artery. The thickened intimal layer on the caudal side of the renal ostium forms an elongated cap (rect-
angle in a). A zone of proteoglycan enrichment (c, green) just below the surface of the caudal ostium surrounds
a densely collagenous core (b, blue) in the intimal “fibrous cap”-like structure. (a) Scale bar = 500 μm; (b and
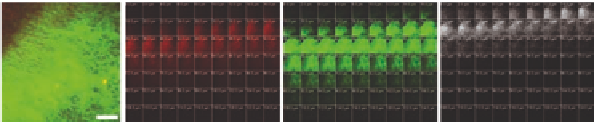
c) Scale bars = 10 μm. (d) LDL binding to renal diverter microstructural components assessed by two-photon
multimodal microscopy. (d) Tiled (9 × 9) two-photon maximum projection of z-series images through 180 μm of
the luminal surface of the aortic entrance to the left renal artery. Merged image. Collagen SHG is green, elastin
autofluorescence is red, and Alexa 647-LDL is blue. LDL binds eccentrically to the collagen-enriched, elastin-poor,
atherosclerosis-susceptible, caudal side of the renal ostium. The tiles (A) and (B) outlined in the cranial and caudal
regions of the renal ostium in (d) are shown to the right in (A) and (B), respectively. Scale bar = 1 mm. (Right)
Z-series images at 0-124 μm from the luminal surface of the aortic wall, for tiles (A) and (B), respectively. Elastin
autofluorescence is red, collagen SHG is green, and Alexa 647-LDL fluorescence is white. Collagen is enriched in
the caudal compared to the cranial ostium. LDL binding is also greatly enhanced in the caudal compared to the
cranial ostium. LDL binding to the surface occurs prior to the appearance of collagen at both the cranial and cau-
dal sites, but overlaps to a considerable extent with collagen in the caudal ostium. Scale bars = 250 μm. (Reprinted
from
Atherosclerosis
211, Neufeld, E. B. et al. The renal artery ostium flow diverter: Structure and potential role in
atherosclerosis, 153-158, Copyright (2010), with permission from Elsevier Ireland LTD.)