Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(typically one frame per second for nonresonant galvos) is inferior to the frame-based wide field micro-
scopy, it offers other powerful imaging capabilities that would not be possible for wide field microscopy
due to the different nature of nonlinear optical imaging contrast mechanisms described in this chapter.
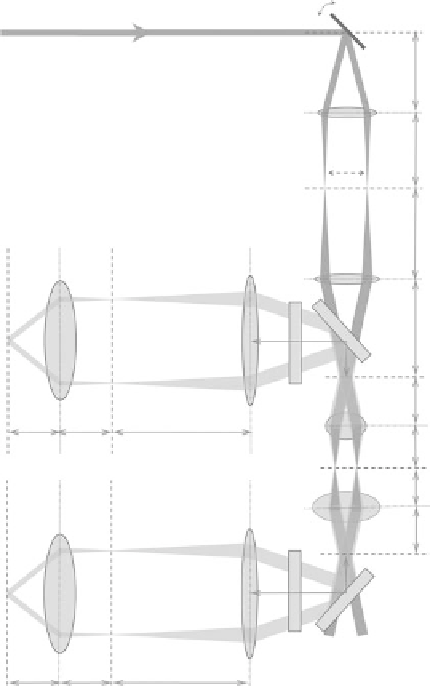
Figure 4.6 displays an ideal schematic of a laser scanning NLO microscope showing the simplest
scanning pattern between point 1 and point 2 with a forward and a backward detection channels which
are optically symmetric with respect to the sample plane. The way the detection is set up differs from
that of a confocal microscope, which has the detector located before the scanning mirror, so that the
emitting ray reverses the propagation of the pump laser beam all the way back through the scan mirror
and the “descanned” ray is then stationary and focused on the confocal pinhole before collection by the
detector. The combination of descanning and a confocal pinhole is essential to achieve 3D sectioning
in confocal fluorescence imaging, but is not necessary for NLO microscopes as there is no out-of-plane
signal. Thus, essentially all NLO microscopes use nondescanned detection by placing the detectors in
a return path where the signal does not traverse the scanning mirrors. Moreover, confocal detection is
highly inefficient and nondescanned detection increases sensitivity by several factors due to the optical
path alone. This sensitivity is increased further for scattering specimens.
SM
f
SL
SL
f
SL
1
2
f
TL
TL
1″
f
TL
DM
BFP
f
OBJ
EF
f
CL
f
CL
f
ETL
2″
OBJ
f
OBJ
SP
2′
1′
DP
CL
EL
f
CD
CD
f
CD
2″′
CFP
DM
1″′
f
CL
f
CL
f
ETL
EF
DP
CL
EL
FIgurE 4.6
Laser scanning microscopy. Light paths are shown for two scan positions (1-1′-1″ (or 1′″)) and
(2-2′-2″ (or 2′″)). The excitation laser beams are in dark gray and the emission light paths are in light gray. SM, scan
mirror; SL, scan lens; TL, tube lens; DM, dichroic mirror; BFP, back focal plane of the objective (OBJ); SP, sample
plane; CD, condenser; CFP, condenser focal plane; EF, emission filter; EL, emission lens; CL, collimation lens; DP,
detection plane.