Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Stem
preCOL-D
Thread
portion
preCOL-NG
Byssus
2 -4 cm
fp-1
fp-4
preCOL-P
Disk
fp-6
fp-2
Ratio
fp-3, -5
Foreign substrata
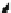
Fig. 9.2
Mussel byssus as complex and hierarchical material from the macroscopic to molecular
levels
biomolecular threads, byssus. Because the animal is tossed about by the sweeping
action of turbulent waves, this mode of holdfast with a centimeter distance from
substratum would latently include several breakpoints. The mussel, however,
overcomes this obstacle due to the fine design of its byssal thread structure from
the meso-/microscopic level to the molecular level [
6
].
The byssal thread has a macroscopically modular structure that includes a thread
portion and an adhesive disk (Fig.
9.2
). The byssal thread overall has an outer coating
in its microscopic level. The adhesive disk is microscopically separated by a bulk layer
and a tip layer, wherein the latter is directly coupled with foreign materials [
7
]. The
coating layer [
8
] and bulk of adhesive disk [
7
] have individual meso-scopic structures,
respectively. Specific localizations of the individual components in the molecular
level also seem to occur. Bulk of the disk [
9
], surface coupling layers at the tip of the
disk [
2
], and outer coating layer [
10
] are actually formed by individual specific
proteins. The thread portion has remarkably distinct physical characteristics proxi-
mally and distally, each of which has different protein compositions [
11
]. Linking
proteins may also occur at junctions of the surface coupling layer and bulk of the disk
[
12
], or between the bulk of the disk and distal end of the thread portion [
13
]. Overall,
these fine, delicate designs support mussel attachment in water.
9.4.1 Unique Proteins in the Byssal Thread
Byssal thread consists of proteins to an extent of 95% in weight, which includes
nine unique proteins, five of which are found at the adhesive disk, three at the thread
portion, and one at the overall outer coating (Fig.
9.3
). Two proteins directly bind to
foreign materials and have molecular weights less than 10 kDa, which are the
lowest ones among all of the proteins. A protein in the bulk of the disk has a






























































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search