Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
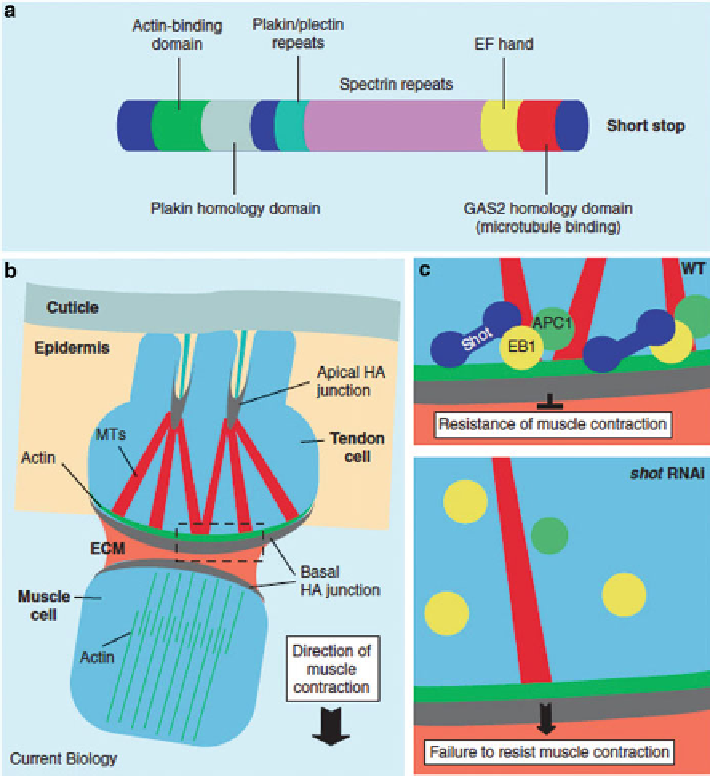
Fig. 6.6 Drosophila
Shot links the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons. (
a
) Diagram of the
various domains of the Shot protein. (
b
) Schematic depicting the tendon cell linking muscle
cells to the exoskeleton. Region outlined with a dotted box represents the region that is enlarged in
(
c
).
MTs
microtubules;
ECM
extracellular matrix;
HA
hemi-adherens junction. (
c
) Model of Shot
function. In the wild type (WT), Shot binds EB1, recruiting it and APC1 to microtubule plus ends,
resulting in resistance to muscle contraction. In the absence of Shot (
shot
RNAi), EB1 and APC1
are lost from microtubule plus ends, and tendon cells fail to resist muscle contraction (note that
some microtubules detach in
shot
RNAi mutants)
claponin-actin binding motifs at its N-terminal domain [
37
,
38
]. Shortstop is highly
expressed in tendon cells, neurons, and ectodermal cells. A tendon-specific knock-
down of Shot using the
stripe
-
gal4
driver leads to larvae that hatch but are incapable
of developing to the third instar larval stage, eventually leading to larval lethality [
39
].
The tendon cells of these larvae are highly elongated, and often tear apart while
maintaining the MTJ (Fig.
6.6
). Molecular analysis has shown that Shot accumulates
Search WWH ::

Custom Search