Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
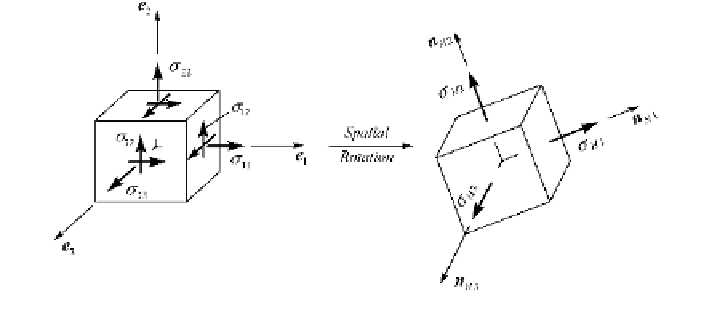
Fig. 3.19
Transformation of the principal axis of the tress tensor
and in matrix notation,
2
4
3
5
h
e
i
e
i
i¼
2
4
3
5
h
n
Hi
n
Hi
i:
r
11
r
12
r
13
r
H1
00
0 r
H2
0
00r
H3
½
S
¼
r
12
r
22
r
23
ð
3
:
101
Þ
r
13
r
23
r
33
In (
3.100
) and (
3.101
) the r
Hi
are the principal direct stress components
(eigen-values) and the n
Hi
are the corresponding (orthonormal) principal directions
(eigen-directions). Scalar (e.g. right) multiplication of (
3.100
) with n
Hk
using n
Hi
n
Hk
¼
d
ik
yields (note that it must not be summed over k on the right-hand side)
!
n
Hk
¼
X
S
n
Hk
¼
X
3
3
r
Hi
n
Hi
n
Hi
r
Hi
ð
n
Hi
n
Hj
Þ
|{z}
d
ik
n
Hk
¼
r
Hk
n
Hk
i
¼
1
i
¼
1
thus the eigen-value problem results in
S
n
Hj
¼
r
Hj
n
Hj
ð
j
¼
1
;
2
;
3
Þ
ð
3
:
102
Þ
where (direction) vectors n
Hj
are sought which are mapped by the operator S into a
multiple of r
Hj
n
Hj
. Using (
3.102
), the identical transformation S
n
Hj
r
Hj
n
Hj
S
n
Hj
r
Hj
I
n
Hj
¼
0 holds, where the following algebraic, homogenous linear
system of equations for the three eigen-vectors n
Hj
is obtained
n
Hj
¼
0
S
r
Hj
I
ð
j
¼
1
;
2
;
3
Þ
ð
3
:
103
Þ
or in full (whereas the n
iHj
(i = 1, 2, 3; j = 1, 2, 3) are the respective coordinates
of the three eigen-vectors n
Hj
with respect to a OBS)