Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
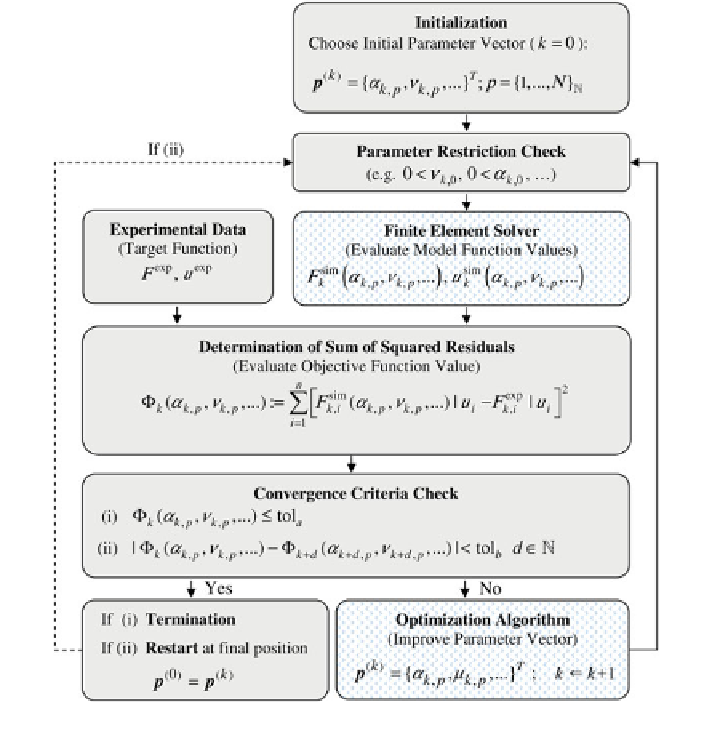
Fig. 3.31
Schematic flow-chart of a single-criteria material parameter optimization process
models, complex geometry and contact interactions under arbitrary loading is the
finite element method. This method is employed to find an approximate solution to
the boundary value problem. In this regard, analytical solution of the set of dif-
ferential equations is only feasible in limited, particular cases. An example is in
uniaxial compression using the Ogden model, whereby however, the model error
increases with increasing lateral material strain.
In addition to evaluating model function values, to iteratively improve the
parameter vector towards minimization of the deviation between computed and
measured quantities, i.e. to solve the least-square problem, an optimization algo-
rithm is needed. A gradient-free algorithm is an appropriate choice. In more
complex situations, as in problems previously described, derivatives of the model
function are not accessible. The algorithm must thus work with objective function
values, exclusively provided by the finite element solver.