Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
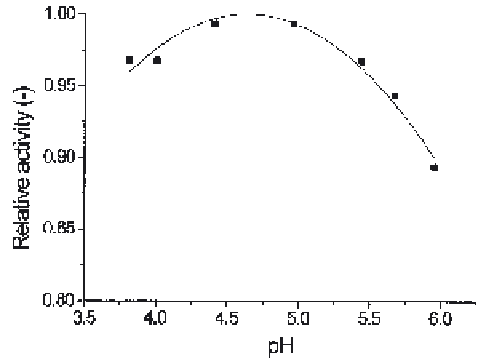
Fig. 11.
Microcalorimetric investigation of pH-activity profile of invertase immobilized on
Eupergit C by direct binding (unpublished results)
5.2
pH-Activity Profiles
The investigation of pH-activity profiles is a typical measurement when a rela-
tive activity change provides sufficient information about the enzyme pro-
perties. Equation (21) reminds us that the actual reaction rate in the column is
directly proportional to the measured thermometric signal, on condition that
the column is packed with a differential amount of IMB. Since the reaction rate
is proportional to the IMB activity, the activity is proportional to the thermo-
metric signal, as well. Therefore, the measurement of the relative change of
thermometric signal due to the pH change can be used instead of conventional
techniques for the investigation of pH-activity.Once more,enzyme flow micro-
calorimetry proves to be a robust,efficient and accurate method.
An example of such a result is illustrated in Fig. 11 showing the pH-activity
profile of invertase immobilized on Eupergit C. The relative activity plotted in
the figure is the ratio of the thermometric signal at given pH divided by the
maximum value of the thermometric signal observed at the pH optimum. The
value of the pH optimum obtained is comparable to the known value for yeast
invertase [38].
5.3
Biocatalyst Stability
As in the case of pH-activity measurement, the investigation of enzyme stabili-
ty is quite often satisfied by obtaining information about the relative decrease of
activity during the enzyme operation,without knowing the absolute value of the
activity during the experiment.Figure 12 shows the stability of invertase bound
Search WWH ::

Custom Search