Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
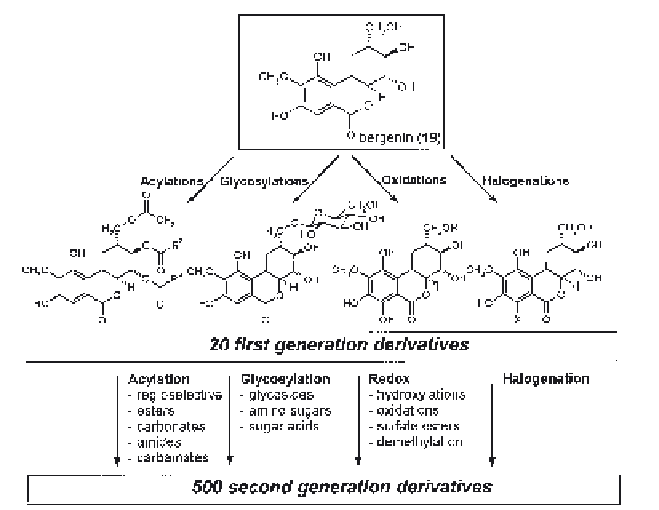
Fig. 12.
Derivatization of bergenin as an example for the concept of combinatorial biocatalysis
disease related genes and gene products.Further estimating that each of these
disease related genes or their products interact with three to ten proteins in the
signaling pathways at least yield 3,000 to 10,000 genes or gene products that are
worth to be tested as potential targets for interaction with effectors oflow-mole-
cular mass.
The identification of disease related targets is one of the most challenging
issues in today's drug research process.Accelerated information on gene struc-
tures is provided by public and private genomic databases providing raw DNA
sequence information on the human genome as well as on the genome ofvarious
animals,plants and microorganisms.Gene sequences from pathogenic bacteria
and fungi attract considerable attention.New targets are urgently requested to
treat infections caused by both,antibiotic resistant microbial strains and novel
types of bacteria such as
Helicobacter pylori
.Actually, the number of disease-
causing bacteria whose genome is completely sequenced by routine DNA
sequencing techniques combined with adjusted data management systems is
growing rapidly.
Traditionally,the approach for the identification of biological targets was a
reductionist one. The pathological phenomenon was examined with increa-
sing resolution typically starting from an understanding of fundamental bio-
logical mechanisms in man or in an animal model.These examinations were
followed by studies involving intact tissues and cells or preparations thereof,
ultimately leading to the identification of molecular targets for drug interac-
tion [323].
Search WWH ::

Custom Search