Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(b)
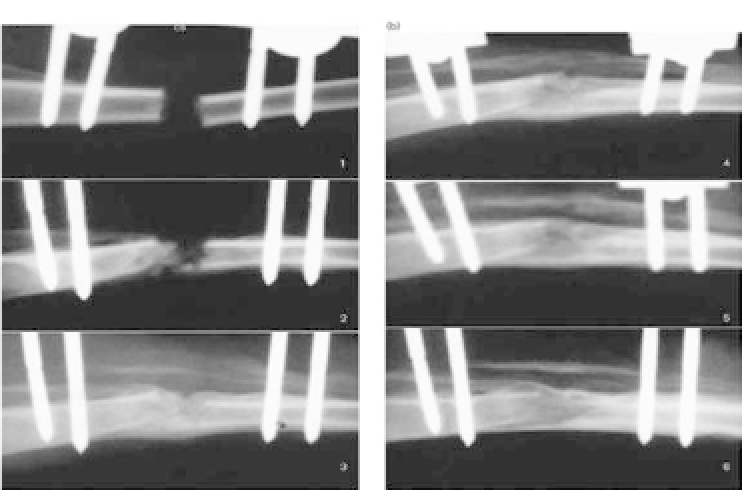
Figure 43.2.
RadiographsofanimalsinexperimentalgroupIwithcalcium
sulfate. There was a faint calcification shadow at the distraction gap at 2
weeks, marked calcification at 4 weeks, and bone bridging in the distracted
area at 6 weeks.
(Fig. 43.1a). After a 3-day postsurgical waiting period, rabbits
underwent distraction at a rate of 1 mm per 12 hours. Distrac-
tion lasted four days with the total lengthening of 8.0 mm. Rab-
bits were randomly divided into three groups. On day 7, group I
was injected with calcium sulfate (Wright Medical Technology Inc,
Arlington, Tennessee, USA) with a carboxy-methylcellulose (CMC)
medium (200 mg calcium sulfate per 1 cm
3
of CMC) in the length-
ening region under fluoroscopic guidance (Fig. 43.1b); group II was
injected with a CMC medium alone as the control; and no injection
was performed in group III. All the rabbits were euthanized 42 days
postsurgery for further analysis.
There was early callus formation at week 4 in group I but not in
groupsIIandIII(Figs.43.2-43.4).Atweek6,alltherabbitsingroup
I had a bony shadow with bridging of the proximal and distal ends
(some rabbits showed mature bone union) in the distracted area.
However,noneoftherabbitsingroupsIIandIIIshowedboneunion.
Furthermore, the bone mineral density (BMD) analysis showed that
at week 3, the percentage BMD of the experimental group I (16.1%)









Search WWH ::

Custom Search