Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
hydrogels.
59
Regardless, collagen gels have shown good
in vivo
and clinical results when combined with progenitor cells and
chondrocytes.
60
,
61
Importantly,forclinicalapplications,thetelopep-
tideshavebeenremovedtoreducethechanceofanadverseimmune
response.
62
-
64
Collagen gels have not been used for zonal cartilage
studies, perhaps due to di
culty in controlling the dimensions of
thegels,butwouldbeinterestingtostudy,especiallyifcollagenfiber
orientation can becontrolled.
36.3.2
Fibrin
Among many different types of matrices, fibrin is the only one
which is inherently produced by a human body for rapid tissue
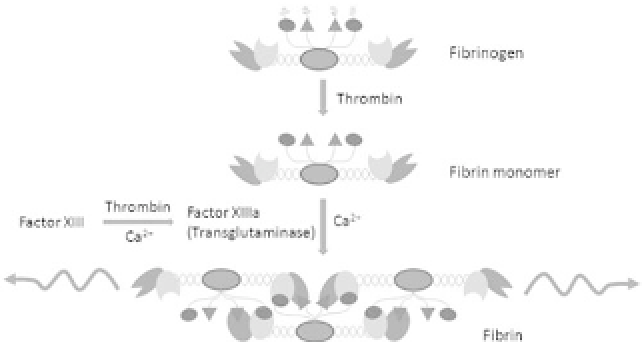
regeneration. During wound healing, fibrin clots are formed by
thrombin-induced cleavage of fibrinogen and Factor XIII, resulting
inFactorXIIIa(transglutaminase)-mediatedcross-linkingofthefib-
rinopeptides (Fig. 36.5). The fibrin clot is a porous structure, with
99.75%ofvoidspace,facilitatinge
cientnutrientexchange.
65
Cells
bind to fibrin (which contains RGD sites), proliferate, and elabo-
rate extracellular matrix, including collagen I.
66
,
67
Naturally, as cells
invade and proliferate the fibrin matrix, they release proteases to
Figure 36.5.
The polymerization mechanism of fibrin (adapted from Ref.
68). Thrombin cleaves peptide fragments from fibrinogen to form fibrin
monomers. These monomers can form covalent bonds between monomers
throughaFactorXIIIa-mediatedreactioninthepresenceofcalciumtoform
a fibrous network that isuseful fortissue engineering.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search