Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
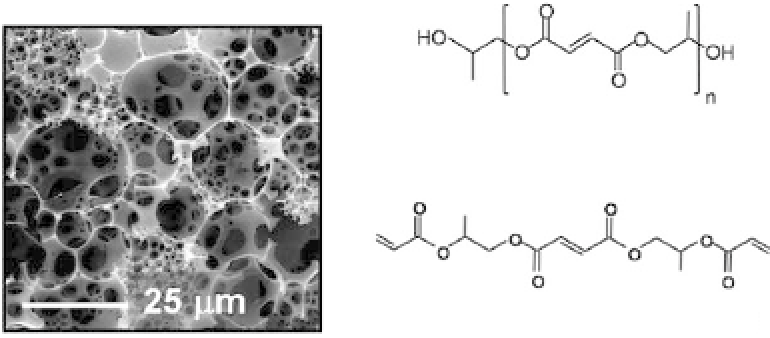
Poly(Propylene Fumarate) (PPF)
Propylene Fumarate Diacrylate (PFDA)
Figure 33.7.
SEM image of fumarate-based polyHIPEs fabricated from
PPF and PFDA. Reprinted with permission from Ref. 37; copyright 2007
American Chemical Society.
addition of a vinyl-based comonomer such as styrene. This resulted
in the first fully biodegradable polyHIPE scaffold.
33.5 New Synthesis Routes
Vinyl monomers copolymerized with a divinyl cross-linker are the
most commonly used systems to generate polyHIPEs.
23
,
36
,
46
,
55
The
resulting monoliths are rigid and relatively brittle. In contrast,
Lepine
et al
. reported the first preparation of polyHIPEs based
on a polyurethane network.
56
This strategy was used to enhance
the elasticity and toughness of the monoliths. Scaffolds of a pure
polyurethane network were found to be too soft and underwent
a high level of shrinkage. The addition of styrene and divinyl-
benzene resulted in the generation of rigid, microcellular IPNs. A
difunctional comonomer, hydroxybutyl methacrylate, was then uti-
lized to create covalent links between the two networks of the IPNs.
As expected, the incorporation of a high concentration (40%) of a
polyurethane (PU) elastomer into the PS rigid network decreased
the modulus and increased the flexibility of the polyHIPE. How-
ever, a lower concentrations (20%) of PU resulted in monoliths
with an increased modulus as compared to the PS network. The
authors hypothesized that this effect was due to an increase in
the proportion of cross-links, which was supported by a threefold








Search WWH ::

Custom Search