Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
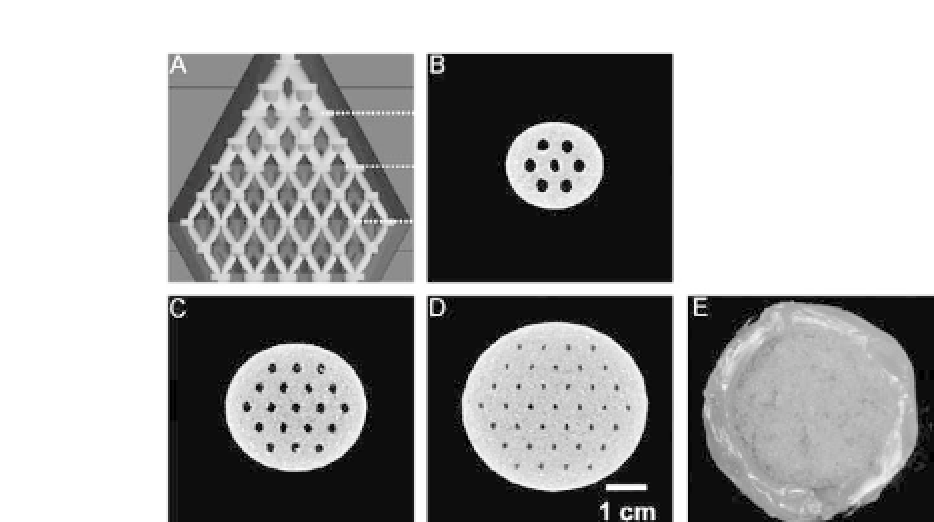
Figure 31.15.
(a) CAD design from front view of a scaffold, (b-d) micro-
computed tomography at the bottoms of second, fourth, and sixth layers of
CAD data, and (e) observation of culture medium flow of a cell-free half-
scaffold.
physicallymixedPEEK/HApowderblendsweresinteredbyvarying
the laser power and temperature settings.
Goodridge
et al
.evaluatedthebiologicalperformanceofaporous
apatite-mullite glass-ceramic to determine its potential as a bone
replacementmaterial.
53
Directcontactandextractassayswereused
to assess the cytotoxicity of the material. A pilot animal study, in
which the material was implanted into rabbit tibiae for four weeks,
was also performed to assess
in vivo
bioactivity. They reported that
the material produced by SLS did not show any acute cytotoxic
effects using either contact orextract methods.
Popov
et al
. have developed surface SLS (SSLS) for bioactive
and bioresorbable scaffold fabrication based on a modified and
enhanced SLS procedure.
54
-
56
SSLS is initiated by melting only the
polymer particle surface but not the poly(D,L-lactic) acid (PLA)
powder, which does not absorb (
σ
ab
<
0.1 cm
-
2
) near-infrared
(
λ
= 0.97 lm) laser radiation. The laser light is absorbed by a small
quantity of homogeneously distributed biocompatible carbon black
(CB) microparticles that are added to the PLA on the surface of







Search WWH ::

Custom Search