Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
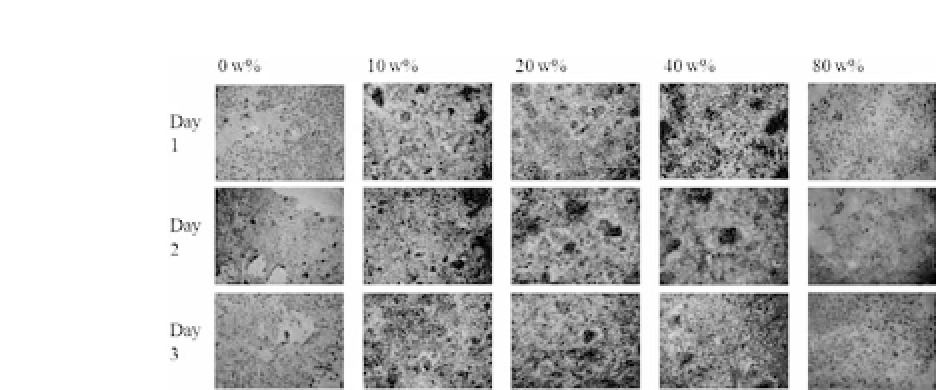
Figure 1.7.
Immunocytochemical staining of RPE cells on PLGA, silk/
PLGA filmafter 1, 2, and 3 days (magnification x100).
31
silk fibroin scaffolds are promising for engineering a range of tis-
sues: bone, ligament, cartilage, skin, nerve, etc. With the advances
of genetic and biochemical engineering, the application of native
silk proteins will expand exponentially in the area of regenerative
medicine and tissue engineering. Figure 1.7 shows the regenera-
tionoftheretinausingPLGA/silkhybridscaffold-seededretinalpig-
ment epithelial (RPE) cells. From the immunocytochemical staining
ofRPEcellsonaPLGA,silk/PLGAfilmafterone,two,andthreedays
with 100 magnification, silk plays an important role for the activa-
tion of the growth and proliferation of RPE cells.
31
1.2.4.6 Hyaluronan
Hyaluronicacid,anaturalglycosaminoglycanspolymer,canbefound
abundantly within cartilaginous ECM. It has some disadvantages
in the natural form, such as high water solubility, fast resorption,
and fast tissue clearance times, resulting in no conduciveness for
biomaterials. In order to overcome these undesirable characteris-
tics, chemical modifications have been done to increase biocompat-
ibility, tailor the degradation rate, control water solubility, and fit
the mechanical property. To increase hydrophobicity, esterification
was carried out to increase the hydrocarbon content of the added
alcohol,resultingintailoreddegradationratessincehydrophobicity
directly influences hydration and the de-esterification reaction.
1
,
20
Another approach such as the condensation reaction between the







Search WWH ::

Custom Search