Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
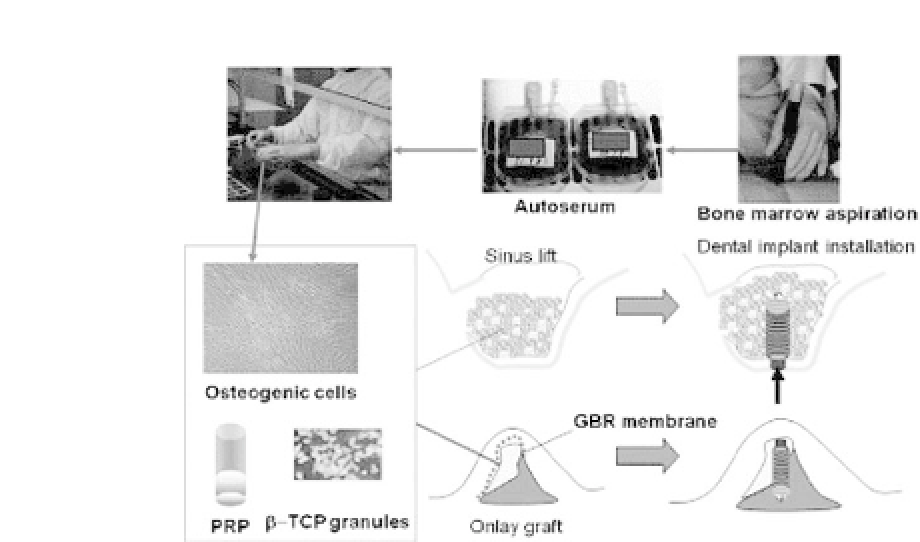
Figure 26.8.
Schematic figure showing the procedure for alveolar bone
tissue engineering. BMSCs were harvested from the iliac crest under local
anesthesia and cultured in a cell culture facility. Nonadherent cells were
discarded. At the time of surgery, cells were detached from flasks and sus-
pended inPRP, which wasturned intoa gel using autologousthrombin. The
gel was then mixed with
-TCP granules as a scaffold and transplanted into
the sinus floorand/or alveolar ridge. See also Color Insert.
β
The results showed that bone regeneration using autologous
BMSC-derived osteogenic cells was feasible (Asahina
et al
., manu-
script under review).
In this study, six months after cell transplantation, bone biop-
sies were performed using a trephine bur at the site of implant
placement. Histology of the regenerated bone was analyzed. Newly
formed bone was observed adjacent to the scaffold as well as
between the scaffolds (Fig. 26.10). The available tissue sample
from patients was from only one time point, so the time course
of scaffold degradation could not be analyzed. However, there
might be two differential types of scaffold degradation, as reported
previously.
4
When the newly formed bone was adjacent to the
scaffolds, it presented as brushlike borders, which may support the
idea that
β
-TCP granules had started to degrade due to resorption
by osteoclastic cells prior to bone regeneration (Fig. 26.9). Some
of the scaffold seemed like it was degraded spontaneously but not







Search WWH ::

Custom Search