Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
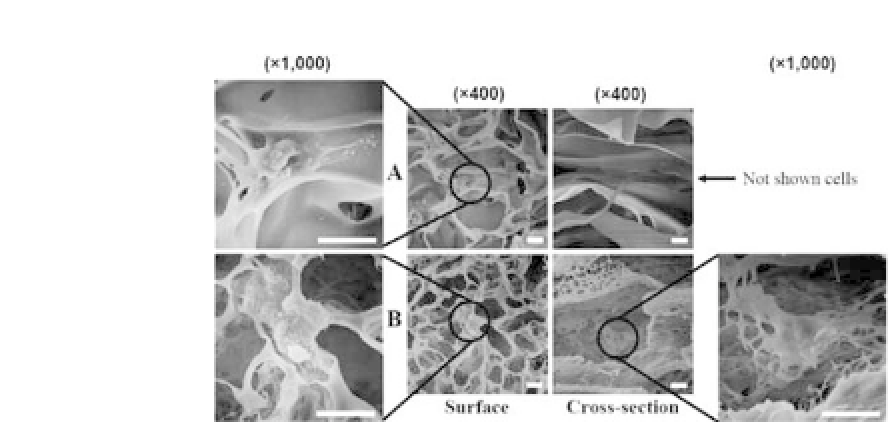
Figure 23.3.
SEM micrographs of the HDFs cultured on chitosan sponge
scaffolds after 7 d of culture. HDFs in the surface/cross section of (a) the CS
scaffoldpreparedbytheTIPSprocessand(b)the
μ
-CSscaffoldpreparedby
the modified TIPS process. (Scale bar= 15
μ
m).
the 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bro-
mide (MTT) assay were that the initial cell adhesion on the
μ
-CS
scaffold was 190% higher than on the CS scaffold. The proliferation
rateofHDFsinthe
μ
-CSscaffoldwas1.82-foldthatintheCSscaffold
after three days of culture.
8
The
μ
-CS chitosan sponge scaffold in which interconnectivity
between pores was improved, compared with the CS scaffold, had
the specific surface area enough for cell attachment and tissue
ingrowth, facilitating a uniform distribution of cells and adequate
transport of nutrients and cellular waste products.
23.4 Chitosan Bead Scaffolds
Bead-type scaffolds can be a large surface to attach and prolifer-
ate cells and easily injected into the body with a syringe if they are
prepared in submicro size. Roh and Kwon fabricated pure chitosan
bead-type scaffolds having various microstructures by an extended
TIPS process.
26
Wu
et al
. reported that a three-dimensional alginate
microbeadplatformwascoatedwithcartilaginousECMcomponents
to emulate thechondrogenic microenvironment,andthe microbead
system promoted bone marrow-derived MSC proliferation and







Search WWH ::

Custom Search