Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3D ECMs induce more effectively hepatocyte functions than two-
dimensional ones.
35
Especially, the design of 3D scaffolds to form
hepatocyte spheroids is very important to enhance liver-specific
functions in liver tissue engineering, because the structure of the
spheroid resembles the tight cell-cell contact in native liver and
tightjunctions,whichmimictheultrastructureofthenativelobule,
36
although the cells in large spheroids experience mass transfer limi-
tationsin the absence ofa vascular network.
Encapsulation of hepatocytes in a biocompatible polymer allows
incorporation of ECM features into the system and permits iden-
tification of encapsulated hepatocytes and analyses of their sur-
vival and function. Also, protection of encapsulated hepatocytes
from immune surveillance
in vivo
is an important advantage of this
system.
37
Yang
et al
.
38
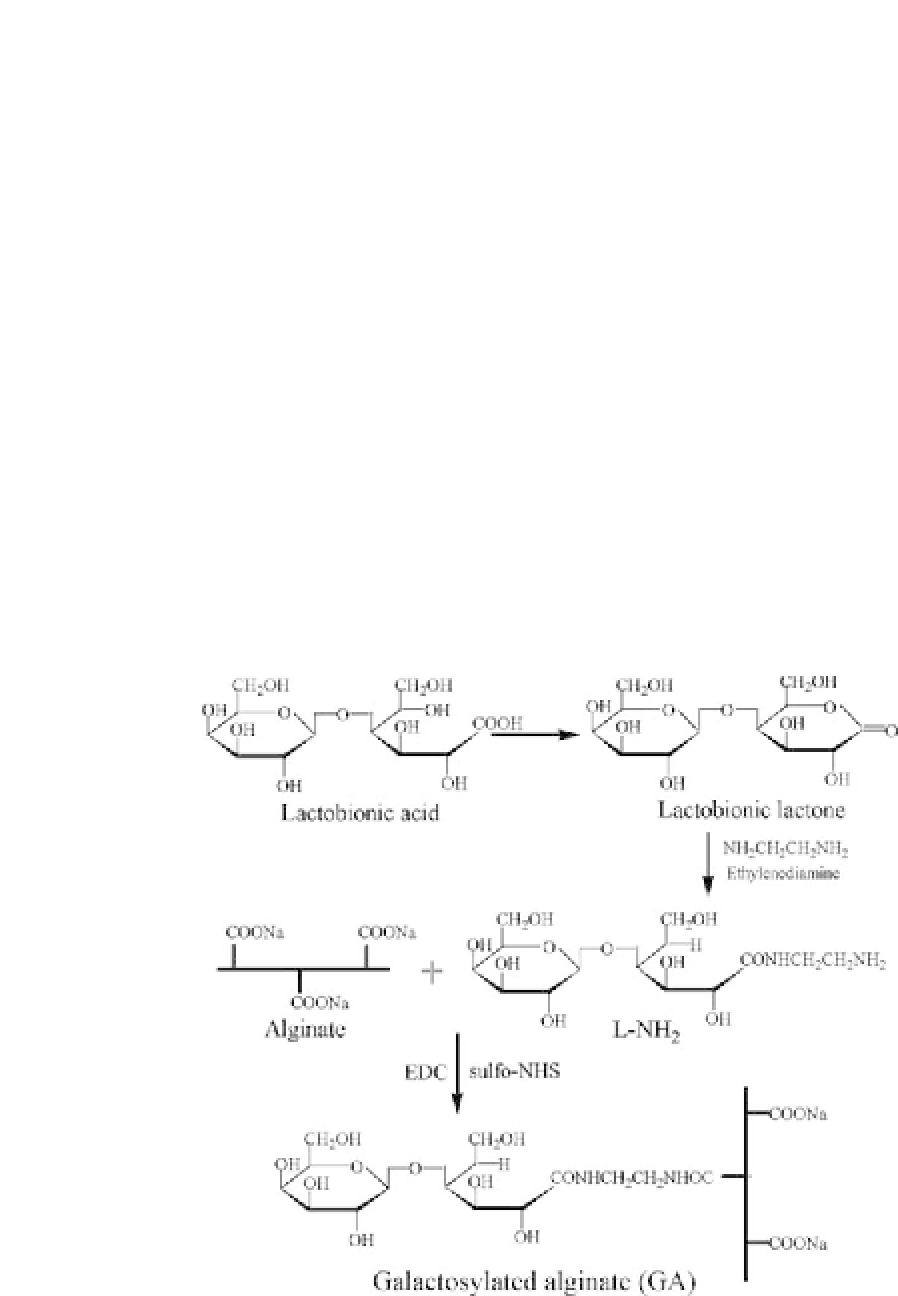
encapsulated hepatocytes in galactosylated
alginate capsules (GAC), as shown in Fig. 21.3. The results showed
that higher cell viability and more spheroid formation of hepato-
cytes were obtained in the GAC than in the alginate capsules (AC).
Figure 21.3.
Reaction scheme of galactosylated alginate (from Ref. 38).







Search WWH ::

Custom Search