Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
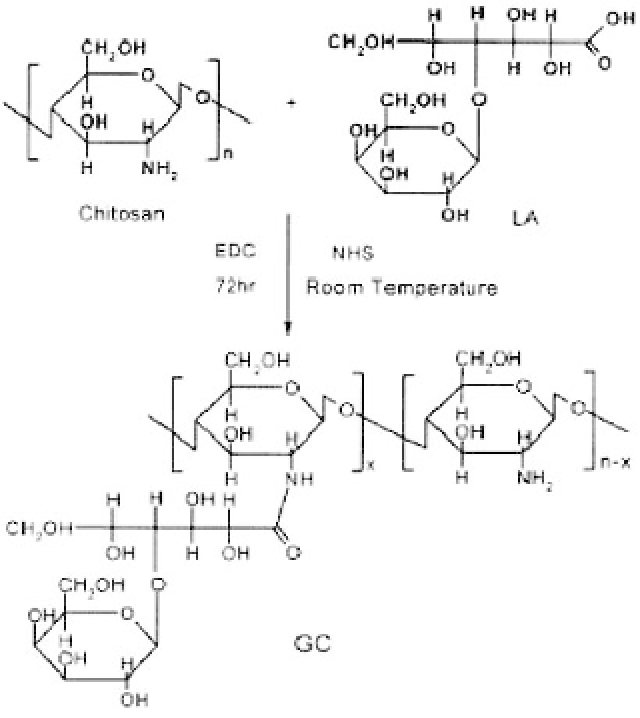
covalently coupled galactose moieties to chitosan, as shown in
Fig. 21.2, to enhance galactose-specific recognition between galac-
tose in the galactosylated chitosan (GC) and ASGPR of hepatocytes.
The hepatocytes adhered to the surface at high concentration of
GC showed round shapes and exhibited spheroid formation after
24 hours in the presence of EGF. Xyloglucan (XG) derived from
tamarind seeds is composed of glucose units in the main chain and
xylose and galactose units in the side chain. Seo
et al
.
28
studied spe-
cific interactions between galactose moieties in the XG and ASGPR
onthehepatocytesadheredtotheXG-coatedPSsurface.Thehepato-
cyte adhesion to the XG-coated surface was dependent on the pres-
ence of Ca
2
+
ions, whereas that to the XG-coated surface could not
be induced by Mg
+
2
ions, suggesting specific interactions between
XG and hepatocytes. Gotoh
et al
.
29
introduced galactose moieties
to silk fibroin (SF) created by the silkworm,
Bombyx mori
.The
Figure 21.2.
Synthesis scheme of GC (from Ref. 27).








Search WWH ::

Custom Search