Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
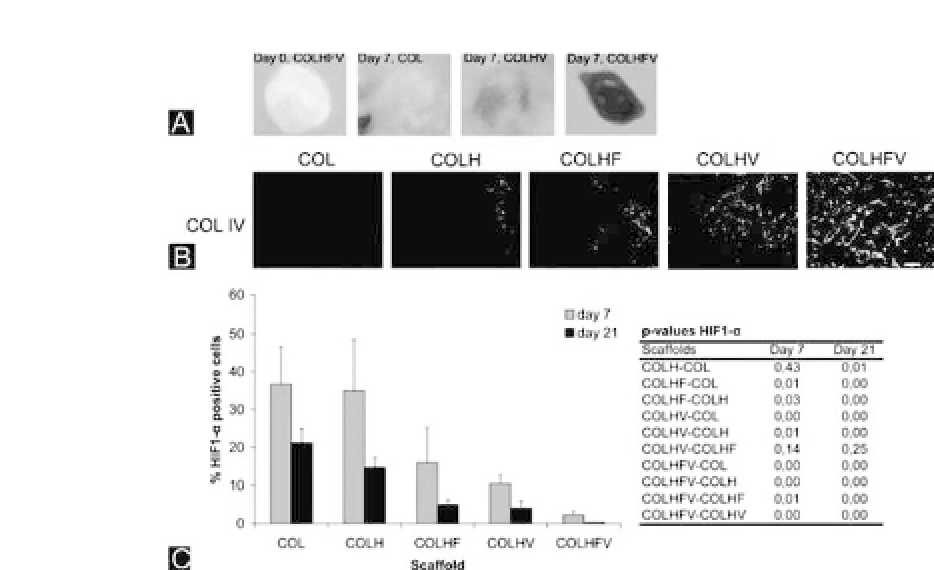
Figure 20.5.
Evaluation of the effect of heparin/growth factors using five
different Col scaffolds.
(a) Macroscopical evaluation of a scaffold before implantation (day 0) and
after implantation for 7 days. Note the red appearance of the Col scaffold
containing heparin, FGF2, and VEGF (COLHFV). (B) Immunohistochemical
evaluation of scaffolds 7 days after implantation and stained for type IV
Col to indicate blood vessels. Note that the Col scaffold containing heparin,
FGF2, and VEGF (COLHFV) shows the most and largest blood vessels.
(c)QuantificationbyHIF1-
α
stainingofthenumberofhypoxiccellspresent
in scaffolds. Note that both at day 7 and day 21, the Col scaffold contain-
ing heparin, FGF2, and VEGF (COLHFV) had significantly fewer hypoxic
cells than all other scaffolds. Bar is 50
μ
m.
Abbreviations
: Col, collagen; H,
heparin;F,FGF-2;V,VEGF.HIF1-
α
,hypoxia-induciblefactor1,alphasubunit.
(Figure reproduced from Nillesen
et al.
2007with permission).
39
To study whether these blood vessels were capable of supply-
ing the cells with oxygen, an immunostaining for hypoxia-inducible
factor 1
α
(HIF1-
α
, part of a heterodimeric transcription factor)
was performed, which stains hypoxic cells. The scaffolds with both
growth factors (COLHFV) possessed significantly lower numbers of
hypoxic cells on both days 7 and 21 compared with all other scaf-
folds (Fig. 20.5c). Already from day 7 on, almost all cells were pro-
vided with enough oxygen, whereas in the plain collagen scaffold







Search WWH ::

Custom Search