Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
20.2 Scaffolds with a Specific Three-Dimensional
Structure
20.2.1
Flat Films
For certain applications, for example, provision of structural sup-
port for epithelial cells (e.g., keratinocytes, urothelial cells), a two-
dimensional structure is su
cient. Epithelia are generally only one
or a few cell layers thick, and the tightly packed cells are resting on
a basement membrane, containing mostly type IV collagen, heparan
sulfate proteoglycan, andlaminins.
10
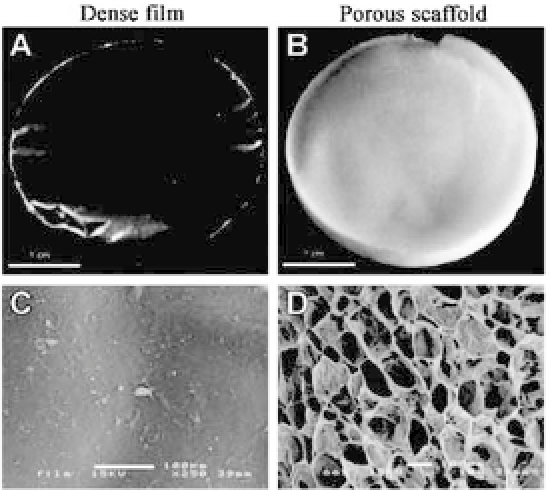
Compact collagen films (Fig. 20.1a) can be prepared by
merely air-drying a homogenized and deaerated collagen suspen-
sion prepared in diluted acetic acid. The concentration of the
collagen suspension will increase when the solvent evaporates.
After evaporation a transparent film layer of the collagen remains,
whichappearsratherdensebyscanningelectronmicroscopy(SEM)
(Fig. 20.1c).
Figure 20.1.
Macroscopic(a,b)andscanningelectronmicroscopicimages
(c, d) of dense films (a, c) and porous scaffolds (b, d). Bar is 1 cm in (a) and
(b)and 100
μ
min(c)and(d).








Search WWH ::

Custom Search