Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
named peptide amphiphiles are arranged in a concentric manner
such that bonds can form among the arranged molecules, which
furtherextendtotheplane'snormaldirection,resultinginnanofiber
morphology. Some biological functional moieties can be introduced
in the peptides design, which can ultimately play important biologi-
cal roles, such as bonemineralization.
14.2.3
Electrospinning
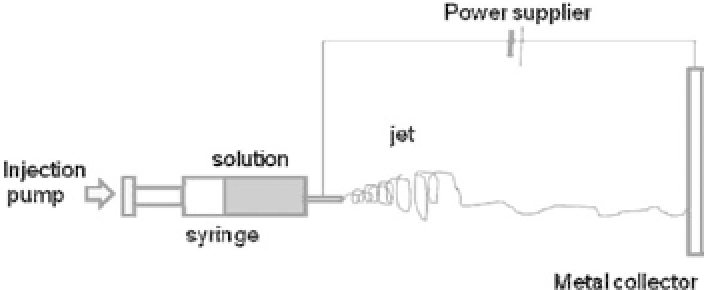
Electrospinning is considered a relatively simple and easy process
to generate nanofibers with cost-effectiveness and mass producibil-
ity. It uses an electric field to spin material dissolved in a solu-
tion. When a high electric field is applied, surface charges collect
at the tip of a needle and overcome the surface tension of the solu-
tion at the tip, becoming a jet and gathering onto a metal collector
(Fig. 14.1). During the electrospinning, the solvent evaporates and
fibrous material is obtained. The obtained fiber sizes range from
tensofnanometerstoafewmicrometers,dependingonthematerial
type and processing variables. Generally the obtained fibrous net-
work is random but can be aligned by modifying processing setups,
suchascollectorparts.Moreover,morphologicalcontrol,suchasthe
creation of nanopores and the core shell structure, is possible by
using porogens and designing a nozzle properly. A range of mate-
rials, mainly polymers, have been electrospun into nanofibers for
medical uses. With its versatility and easy setup, research on elec-
trospinning isgrowing rapidly in the tissue regeneration area.
Power supplier
jet
solution
Injection
pump
syringe
Metal collector
Figure 14.1.
Schematic illustration of the electrospinning process to gen-
erate nanofibers.












Search WWH ::

Custom Search