Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 13.1. Electrospinning conditions for various amounts of polymer
solution
Distance
∗
(cm)
Concentration (wt%)
Voltage (kV)
Flow rate(mL/h)
PHBV
2
7
15
1.5
PHBV-Col
2
12
22
1.0
Collagen
3
20
15
1.5
∗
Distance is from thespinneret to thecollector.
a grounded collector, the solvent evaporated and a charge polymer
fiber was deposited on the collector in the form of a nanofiber web.
Nanofibers with various proportions of PHBV and collagen (7:3,
5:5, and 3:7) were prepared. Nanocomposite mats with more than
50%collagenwerefragile.Therefore,7:3PHBV-Colwasusedinthis
study (Table13.1).
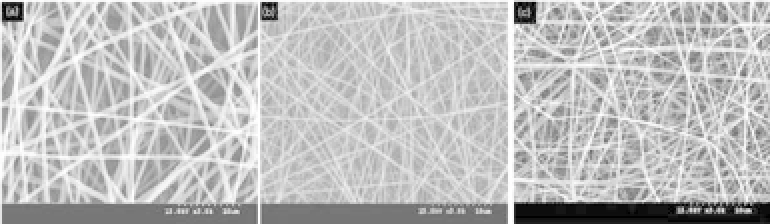
The resulting fibers varied from 300 to 600 nm in diameter. The
images demonstrate continuous fiber morphology, and the compos-
ite fibersdo notcontain beads (Fig. 13.2).
To study the surface morphology of PHBV and PHBV-Col
nanofibers, the surface was imaged by a tapping mode using an
atomic force microscope (AFM) (Fig. 13.3). The collagen nanofiber
was so fragile that AFM observation was not possible. The PHBV
nanofiber surface (Fig. 13.3a) showed a relatively homogeneous
image, while PHBV-Col (Fig. 13.3b) showed a heterogeneous image.
The presence of collagen in PHBV was considered to have induced
such heterogeneity.
Figure 13.2.
SEM micrographs of nanofibrous scaffolds; (a) PHBV,
(b)PHBV-Col, and (c) collagen (adaptedfrom Ref. 16).











Search WWH ::

Custom Search