Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
vapor, it should be reactive with toxic gases and chemicals, it should
be insoluble in solvents, and it should be lightweight. As discussed
before, due to the very small pore size of nanofiber matrices, they
provide an impermeable barrier to toxic chemical agents. Also the
high surface-area-to-volume ratio of nanofibers enables them to
formlightweightfabricswithremarkablebreathingproperties.
4
Due
to the simplicity and versatility of the electrospinning process, con-
ductive fibers can be fabricated from polymers with unusual elec-
trical, electronic, ionic, photoelectric, and piezoelectric properties.
Thesefiberscouldbeusedinthefabricationofnovelnanoelectronic
devices, nanoelectronic machines, and sensors for high-technology
applications.
6
In electrospinning, polymer solutions are deposited as fibrous
matrices, in which chain entanglements in a su
ciently high-
polymer concentration in solution produce continuous fibers.
7
Although the process of electrospinning has been known for some
time,
8
and attempts have been made previously to make vascular
grafts using this technique,
9
the application of electrospun fibers as
scaffolds for tissue engineering has recently investigated by many
researchers.
3
,
5
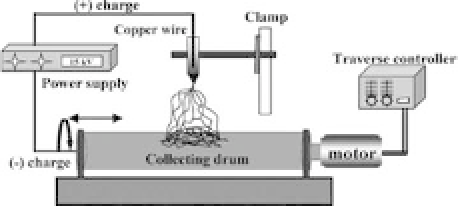
The prototype electrospinning setup that has been
employedinthisstudyisillustratedschematicallyinFig.12.1,which
consistsofasyringe,agroundelectrode(aluminumsheetonarotat-
ing drum) 10-15 cm from the needle, and a high-voltage power
supply. Jet initiation is achieved by charging the polymer solution,
followedbyinjectionthroughthecapillarytipwithatipdiameterof
0.5 mm. Because of its charge, the ejected solution is drawn toward
the collector as a whipping jet.
10
During the jet's travel, the solvent
Figure 12.1.
A schematic of electrospinning. Reprinted from Ref. 10 with
permission from Elsevier.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search