Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Figure 9.22.
Cross-linking reaction. The reaction between HA-aldehyde
(HAA) and PVA-hydrazide (PVAH) is highly selective and results in the for-
mation of a network held together by stable hydrazone bonds.
75
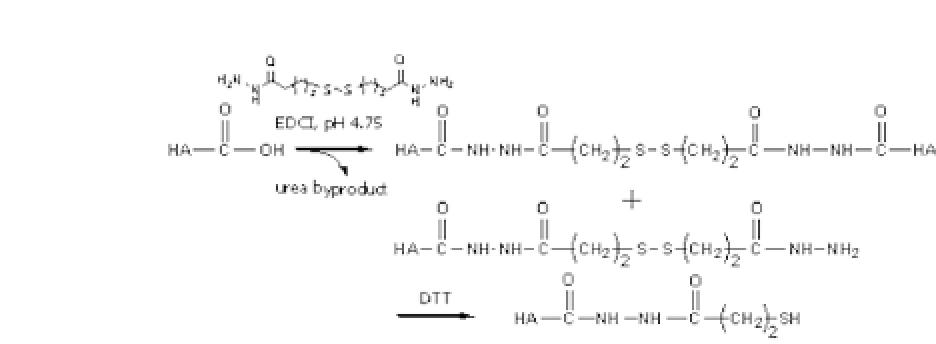
with sodium
tetra
-thionate, 3,3-
di
-thiobis(propanoic hydrazide), or
di
-vinyl sulfone with the hydroxyl groups of HA and then reduced
with reducing agents such as DTT.
23
,
76
Detailed chemical mecha-
nisms of Michael-type reactions have been reported elsewhere by
theauthor.
77
Thevinylsulfonegroupsreactquiterapidlyundermild
conditions (pH 7, room temperature) with thiol groups, resulting in
cross-linked hydrogels. The properties of the thiol-modified HA gel
could be controlled by 1) the molecular weight of starting HA, 2)
the degree of grafted of thiols and (metha)acrylates among other
factors.
27
9.4.1.5 HA-aldehyde hydrogels
By utilizing the reaction mechanisms that both formaldehyde and
glutaraldehyde cross-link proteins via amine-grafted HA deriv-
atives for tissue preservation and regeneration,
25
,
68
grafting of
formaldehyde to low molecular weight HA was used to create a
cross-linked HA hydrogel, Biomatrix's Hylan-A that is water soluble
butmoreviscousandelasticthannativeHA.
21
,
43
The
in situ
reaction
through Schiff's base formation of aldehyde groups of the oxidized
low molecular weight HA with amino residues of collagen II in the
counterpart polymer was used for the preparation of self-cross link
hydrogels for intervertebral disc tissue engineering. The gelation







Search WWH ::

Custom Search