Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
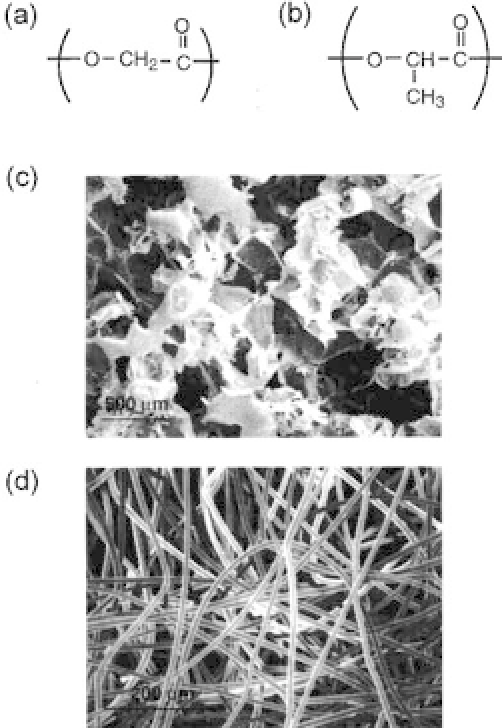
Figure 8.2.
Chemical structure of (a) poly(glycolic acid), (b) poly(lactic
acid),typicalstructuresof(c)porousscaffoldsofpoly(lactide-
co
-glycolide),
and (d) nonwoven fabrics of poly(glycolic acid). These latter materials have
been widely used for tissue engineering applications. (Reprinted from Ref.
12; copyright 1998 John Wiley &Sons, Inc.).
metabolites, and growth factors.
10
To date, various types of poly-
mers have been studied and utilized in tissue engineering.
11
Aliphatic polyesters, including poly(glycolic acid) (PGA), poly(lactic
acid) (PLA), and the copolymer polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA)
of these materials, are the most widely used synthetic polymers
(Fig. 8.2).
12
,
13
These polymers have a long history of use in medical
applications and are considered safe in many situations by the Food
and Drug Administration (FDA). However, the use of these types of
polymerscaffoldsrequiresthesurgeontomakeincisions(cuts)suf-
ficiently large to enable placement of the polymer/cell constructs.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search