Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.4 Dry stretch process for manufacture of hollow fibre blood oxygenation
membranes.
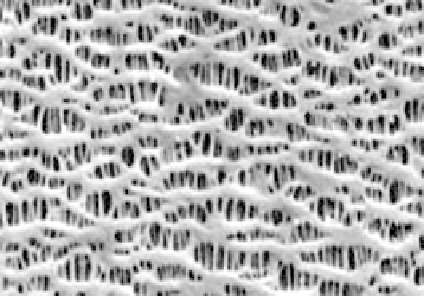
By this annealing and stretching process, the tight capillary wall is ruptured to
build pores. Of course the properties of the raw capillary and the conditions of
the various stretching and annealing steps need to be adjusted very carefully to
yield pores of the desired shape and in the target range of pore size. In the
scanning electron micrographs (SEMs) in Fig. 1.5 the direction of the stretching
process is in the vertical direction: the pores exhibit a lengthy shape into the
direction of the stretch.
This process yields a membrane that has good mechanical stability and is
ideal for demanding textile make-up such as winding at elevated speed. By
adjusting the temperatures and forces, the pores can be generated in a way that
means plasma breakthrough is not an issue.
The same technology can of course also be applied to films of PP, so that flat
sheet membranes can be produced according to the same scheme. Such mem-
1.5 SEM of oxygenation membranes produced by dry stretch.