Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
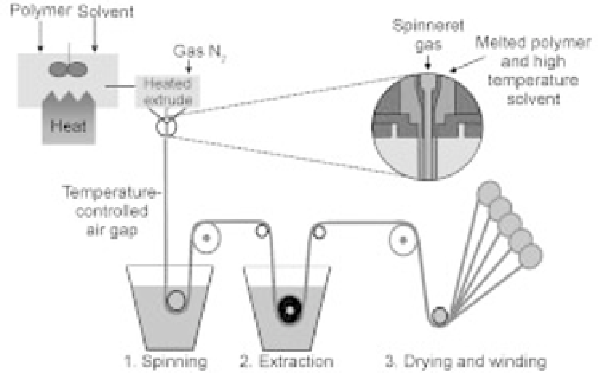
1.2 Thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) process for manufacture of
hollow fibre blood oxygenation membranes.
polymer (PP or PMP) is dissolved in a hot mixture of solvents (mostly natural
oils) and then pumped through a ring-shaped spinneret, with gas being blown
through a circular opening in the centre of the spinneret, concentric with the
ring, to keep the lumen of the capillary open. The solvent system needs to be
composed so that the polymer is soluble in a hot mixture of the solvents, but not
in a cold mixture: when the hot solution exits the heated spinneret, it is cooled
down and the polymer is thermally induced to precipitate (recrystallise) to form
the membrane wall. This crystallisation process needs to start in many nuclea-
tion centres homogeneously distributed through the polymer solution and to
proceed quickly, so that the solvent mixture is trapped in many tiny droplets
throughout the membrane wall that is created. These droplets need to be
connected with each other: after the cooling step, the membrane is extracted
with a suitable solvent such as alcohol to wash out all oil and oil residues. A fine
network of pores penetrates the membrane wall where the oil has been. The
membrane exhibits a sponge-like structure (Fig. 1.3).
Depending on the exact conditions (composition of the solvent system, tem-
perature, temperature gradients, cooling from outside only or inside and outside,
spinning speed, pressures, etc.), the membrane structure can be influenced to
yield membranes with larger or smaller pores, with symmetrical structures (i.e.
constant pore size throughout the whole wall thickness) or asymmetrical struc-
tures, development of an outer or inner skin, tortuosity of the pores, etc. After
the washing step, the membrane is dried and wound on spools for further
processing.
This process yields a membrane that can be produced with very high porosities
(exceeding 50% by volume) and at the same time very high tortuosity of the
pores, so that the membrane is very resistant to blood plasma breakthrough.