Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CHAPTER 5
Neural Branches
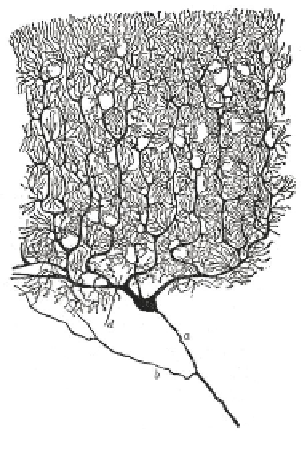
In Ch. 4, we considered propagation in uniform and straight cables. Figure 5.1 shows the complex web
of dendrites that is collectively called the
dendritic tree
. It is clear that the tree contains branching cables,
changes in diameter and curves. In this chapter we will generalize cable theory to handle changes in
membrane properties and branching. We will first examine a method of simplifying the tree by
lumping
the dendrites into one large compartment. We will then turn to the more sophisticated method of
multicompartment
models.
Figure 5.1:
Dendritic tree.
5.1 LUMPEDMODELS
Lumped models were developed before computers became available as a way to simplify a complex neuron
to a single unit. The goal was to make analytical predictions about the behavior of neurons.
5.1.1 The Rall Model
To model the complex dendritic tree, Rall recognized that the branching dendrite was simply acting
as a receiver for many inputs and then attenuating the input. He therefore proposed that the dendritic
tree could be collapsed down to one signal passive cable of varying diameter. This would mean that the
dendritic tree could be represented by an
equivalent
cable as shown in Fig. 5.2. Likewise, the various