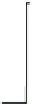Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
m
0
)e
−
t/τ
m
(B)
m(t)
=
m
∞
(B)
−
(m
∞
(B)
−
(3.24)
(A))e
−
t/τ
m
(B)
.
m(t)
=
m
(B)
−
(m
(B)
−
m
(3.25)
∞
∞
∞
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
WLPHPVHF
Figure 3.6:
m-gate changes over time for changes in holding potential.
is the target for
m
and
τ
m
is the rate at which this new
target is reached. To demonstrate this idea, Fig. 3.6 shows three changes in
V
h
with the corresponding
change in
m
. It may be helpful to think about how Figs. 3.5 and 3.6 are related.
The intuitive interpretation is that
m
∞
3.1.7 AGame of Tag
An analogy to the steady-states and time constants may be thought of as a game on an obstacle course.
You and 100 of your friends all have the goal of reaching a diamond that will be set somewhere on the
course. You can imagine that if the diamond stays in one location, you would simply navigate through
water, hoops, sand, and gravel to get to it. Although this may take time, eventually you would all reach
the diamond.The location of the diamond therefore is analogous to the steady state. If the location of the
diamond, however, suddenly changed, you and your friends would again set out across the course to reach
it. The type of obstacles in your way (not necessarily the distance) would determine how long it takes
to reach the diamond. The way that your time to reach the diamond is dependent upon the obstacles in
your way is analogous to the time constant. Now imagine that the diamond is moving around the course,
suddenly appearing in one location and then quickly moving to a new location, faster than you and your
friends can keep up.
Next imagine that at the same time that you and your friends are chasing a diamond, another group
of 101 people are also chasing a ruby, and a third set of 101 people are chasing an emerald. Here, the
analogy is at the diamond is the
m
-gate, the ruby is the
h
-gate, and the emerald is the
n
-gate. Although
our game is not a perfect analogy to the dynamics of gates, it may help understand the next section where
the Hodgkin-Huxley action potential is examined.