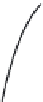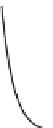Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
ï
T
7LPHPVHF
7LPHPVHF
Figure 2.5:
Charging and discharging of a passive membrane.
2.3 STRENGTH-DURATIONRELATIONSHIP
To perform our analysis of the passive membrane we assumed that
V
m
<V
t
m
. It would therefore be
helpful to know in what situations our assumption is valid. Examining Eq. (2.15),
V
m
(t)
during the
stimulus is dependent on
V
R
m
C
m
. Consider that
I
stim
may be small such that
V
∞
<V
t
m
. In this case, the stimulus may remain on forever and
V
m
will charge up to a steady state value
below
V
th
. In other words, the membrane will remain passive. If
I
stim
is steadily increased, eventually
V
∞
=
I
stim
R
m
and
τ
m
=
∞
will be equal to
V
t
m
. In this case, the steady state will level out exactly at the threshold but it may take
a very long time for
V
m
will clearly be greater than
V
t
m
. As the right side of Fig. 2.5 indicates, however, even if
V
∞
>V
t
m
the stimulus may be on for such
a short time that the membrane does not have time to charge to the threshold. It follows that there is an
interplay between the strength of
I
stim
and the duration of
I
stim
, which can be represented graphically in
a
strength-duration
plot. Given a constant value for
V
t
m
, Fig. 2.6 shows the combinations of strength and
duration that exactly charge the membrane to the threshold. Mathematically, we can set
V
m
=
V
t
m
to reach threshold. If
I
stim
is increased further,
V
∞
and
substitute into Eq. (2.15)
V
t
m
e
−
D/τ
m
)
=
−
I
stim
R
m
(
1
(2.17)
where
D
is the duration of the stimulus. One interesting limit is to find the minimum current that can
bring the membrane to
V
t
m
.If
D
→∞
V
t
m
=
I
stim
R
m
(2.18)
V
t
m
R
m
I
stim
=
I
rhe
=
(2.19)
which explains the value of asymptote in Fig. 2.6. This value is called
rheobase
,
I
rhe
, and is a measure of
current. Another important measure can be derived by assuming that we apply two times the rheobase
current to find the corresponding time to charge the membrane to
V
t
m
.
V
t
m
e
−
D/τ
m
)
=
2
I
rhe
R
m
(
1
−
(2.20)